Sequential Approach for Water Purification Using Seashell-Derived Calcium Oxide through Disinfection and Flocculation with Polyphosphate for Chemical Pollutant Removal
- PMID: 38524416
- PMCID: PMC10955710
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07627
Sequential Approach for Water Purification Using Seashell-Derived Calcium Oxide through Disinfection and Flocculation with Polyphosphate for Chemical Pollutant Removal
Abstract
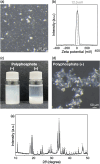
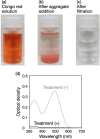
Safe water supply is usually inadequate in areas without water treatment plants and even in a city under emergency conditions due to a disaster, even though safe water is essential for drinking and other various purposes. The purification of surface water from a river, lake, or pond requires disinfection and removal of chemical pollutants. In this study, we report a water purification strategy using seashell-derived calcium oxide (CaO) via disinfection and subsequent flocculation with polyphosphate for chemical pollutant removal. Seashell-derived CaO at a concentration (2 g L-1) higher than its saturation concentration caused the >99.999% inactivation of bacteria, mainly due to the alkalinity of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) produced by hydration. After the disinfection, the addition of sodium polyphosphate at 2 g L-1 allowed for the flocculation of CaO/Ca(OH)2 particles with adsorbing chemical pollutants, such as Congo red, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate, and polychlorinated biphenyls, for removing these pollutants; purified water was obtained through filtration. Although this purified water was initially highly alkaline (pH ∼ 12.5), its pH decreased into a weak alkaline region (pH ∼ 9) during exposure to ambient air by absorbing carbon dioxide from the air with the precipitating calcium carbonate. The advantages of this water purification strategy include the fact that the saturation of CaO/Ca(OH)2 potentially serves as a visual indicator of disinfection, that the flocculation by polyphosphate removes excessive CaO/Ca(OH)2 as well as chemical pollutants, and that the high pH and Ca2+ concentrations in the resulting purified water are readily decreased. Our findings suggest the usability of seashell-derived material-polymer assemblies for water purification, especially under emergency conditions due to disasters.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluating the influence of pH adjustment on chemical purification efficiency and the suitability of industrial by-products as alkaline agents.J Environ Manage. 2018 May 1;213:180-188. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.067. Epub 2018 Feb 27. J Environ Manage. 2018. PMID: 29494934
-
Microbial and cod removal in a municipal wastewater treatment plant using coagulation flocculation process.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2002 Sep;37(8):1483-94. doi: 10.1081/ese-120013271. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2002. PMID: 12369640
-
Preparation and characterization of TiO2 generated from synthetic wastewater using TiCl4 based coagulation/flocculation aided with Ca(OH)2.J Environ Manage. 2019 Nov 15;250:109521. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109521. Epub 2019 Sep 11. J Environ Manage. 2019. PMID: 31521035
-
ZeroCAL: Eliminating Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Limestone's Decomposition to Decarbonize Cement Production.ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2024 Oct 10;12(43):15762-15787. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.4c03193. eCollection 2024 Oct 28. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2024. PMID: 39483210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solar-Enhanced Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Treatment: Simultaneous Removal of Pathogens and Chemical Pollutants.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Aug 14;12(8):9542-61. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120809542. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26287222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee A.; Elam J. W.; Darling S. B. Membrane Materials for Water Purification: Design, Development, and Application. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 17–42. 10.1039/C5EW00159E. - DOI
-
- Werber J. R.; Osuji C. O.; Elimelech M. Materials for Next-Generation Desalination and Water Purification Membranes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1601810.1038/natrevmats.2016.18. - DOI
-
- Singh N. B.; Nagpal G.; Agrawal S.; Rachna Water Purification by Using Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 11, 187–240. 10.1016/j.eti.2018.05.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
