A sodium alginate - silk fibroin biosponge loaded with thrombin: Effective hemostasis and wound healing
- PMID: 38524596
- PMCID: PMC10958712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28047
A sodium alginate - silk fibroin biosponge loaded with thrombin: Effective hemostasis and wound healing
Abstract
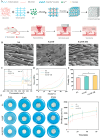
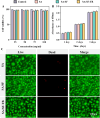
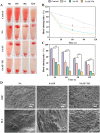
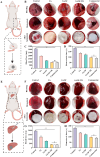
In trauma first aid, rapid hemostasis is a priority, extricating patients from hemorrhagic shock and infection risks. This paper explores novel hemostatic materials, using ion-crosslinking and freeze-drying techniques. Iterative experiments determined optimal conditions for the temperature-variable mixing-freeze-drying chemical reaction of sodium alginate (SA)/silk fibroin (SF). We used SA, SA/SF, SA/SF-TB and commercial hemostatic sponge control samples to perform hemostasis experiments on rat liver injury and femoral artery injury models, and to perform wound healing experiments on rat back full-layer skin. The results showed that the hemostatic time and blood loss of SA/SF-TB group rats (liver hemorrhage model: 397.17 ± 34.80 mg, 77.83 ± 7.41 s; Femoral artery bleeding model: 940.33 ± 41.93 mg, 96.83 ± 4.07 s) was significantly better than other experimental groups, and similar to the commercial group. The wound healing experiment showed that the new granulation tissue thickness of SA/SF-TB group was thicker (380.39 ± 28.56 μm) at day 14. In addition, the material properties and biocompatibility of sponges were characterized by cell experiments and in vivo embedding experiments. All the results showed that the SA/SF-TB hemostatic sponge prepared in this study could not only seal the wound quickly and stop bleeding, but also promote the growth of epidermal cells and fibroblasts and accelerate wound healing. This new material solves the shortcomings of traditional materials such as low stability, limited shelf life, high unit price, and has good biocompatibility, easy preparation, rapid hemostasis and other excellent properties. Therefore, this innovative hemostatic material has great prospects and potential in clinical applications.
Keywords: Compound hemostatic sponge; Hemostatic method; Silk fibroin; Sodium alginate; Thrombin; Trauma.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Dai C., Yuan Y., Liu C., Wei J., Hong H., Li X., Pan X. Degradable, antibacterial silver exchanged mesoporous silica spheres for hemorrhage control. Biomaterials. 2009;30:5364–5375. - PubMed
-
- Huang W., Wu J., Huang Z., Zhang D., Chen F., Liu C. A self-gelling starch-based sponge for hemostasis. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2023;11:1331–1343. - PubMed
-
- Iwano K., Toyonaga H., Katanuma A. Achieving hemostasis during endoscopic necrosectomy for walled-off pancreatic necrosis using gel immersion technique. Dig. Endosc. 2022;34:e105–e106. - PubMed
-
- Wang J., Li C., Zhang W., Huang W., Liu Z., Shi R., Wang S., Liu S., Shi W., Li Y., Xu L. A contact-polymerizable hemostatic powder for rapid hemostasis. Biomater. Sci. 2023;11:3616–3628. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

