Comparison of seven anthropometric indexes to predict hypertension plus hyperuricemia among U.S. adults
- PMID: 38524637
- PMCID: PMC10958198
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1301543
Comparison of seven anthropometric indexes to predict hypertension plus hyperuricemia among U.S. adults
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to compare the association of hypertension plus hyperuricemia (HTN-HUA) with seven anthropometric indexes. These include the atherogenic index of plasma (AIP), lipid accumulation product (LAP), visceral adiposity index (VAI), triglyceride-glucose index (TyG), body roundness index (BRI), a body shape index (ABSI), and the cardiometabolic index (CMI).
Methods: Data was procured from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which recruited a representative population aged 18 years and above to calculate these seven indexes. Logistic regression analysis was employed to delineate their correlation and to compute the odds ratios (OR). Concurrently, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were utilized to evaluate the predictive power of the seven indexes.
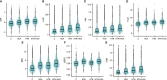
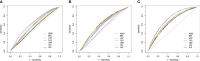
Results: A total of 23,478 subjects were included in the study. Among these, 6,537 (27.84%) were patients with HUA alone, 2,015 (8.58%) had HTN alone, and 2,836 (12.08%) had HTN-HUA. The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the AIP, LAP, VAI, TyG, BRI, ABSI, and CMI were all significantly associated with concurrent HTN-HUA. The OR for the highest quartile of the seven indexes for HTN-HUA were as follows: AIP was 4.45 (95% CI 3.82-5.18), LAP was 9.52 (95% CI 7.82-11.59), VAI was 4.53 (95% CI 38.9-5.28), TyG was 4.91 (95% CI 4.15-5.80), BRI was 9.08 (95% CI 7.45-11.07), ABSI was 1.71 (95% CI 1.45 -2.02), and CMI was 6.57 (95% CI 5.56-7.76). Notably, LAP and BRI demonstrated significant discriminatory abilities for HTN-HUA, with area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.72 (95% CI 0.71 - 0.73) and 0.73 (95% CI 0.72 - 0.74) respectively.
Conclusion: The AIP, LAP, VAI, TyG, BRI, ABSI, and CMI all show significant correlation with HTN-HUA. Notably, both LAP and BRI demonstrate the capability to differentiate cases of HTN-HUA. Among these, BRI is underscored for its effective, non-invasive nature in predicting HTN-HUA, making it a superior choice for early detection and management strategies.
Keywords: NHANES (National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey); adults (MeSH); anthropometric indexes; hypertension; hyperuricemia.
Copyright © 2024 Li and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triglyceride Glucose Index Is More Closely Related to Hyperuricemia Than Obesity Indices in the Medical Checkup Population in Xinjiang, China.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 2;13:861760. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.861760. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35311243 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting hypertension by obesity- and lipid-related indices in mid-aged and elderly Chinese: a nationwide cohort study from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Apr 20;23(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03232-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37081416 Free PMC article.
-
[Associations Between Insulin Resistance Indexes and Hyperuricemia in Hypertensive Population].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2023 Jun;45(3):390-398. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.15414. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37407524 Chinese.
-
Association between anthropometric indices and hyperuricemia: a nationwide study in China.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Mar;43(3):907-920. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06884-w. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38315297
-
Association of body roundness index with cardiovascular disease in patients with cardiometabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES 2009-2018.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 3;16:1524352. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1524352. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39963283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship of cardiometabolic index with bowel movement frequency: an NHANES-based cross-sectional analysis.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Apr 24;24(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02567-w. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40275266 Free PMC article.
-
Association between visceral adiposity index and hyperuricemia and gout among US adults: a cross-sectional analysis of NHANES 2007-2018.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22196. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08138-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595266 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Body Roundness Index and A Body Shape Index with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: insights from NHANES 2015-2018 data.Front Nutr. 2024 Nov 18;11:1492673. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1492673. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39624686 Free PMC article.
-
Association between cardiometabolic index and frailty among patients with diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2024 Dec 6;11:1495792. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1495792. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39713778 Free PMC article.
-
How does biological age acceleration mediate the associations of obesity with cardiovascular disease? Evidence from international multi-cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 May 14;24(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02770-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40369582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fryar CD, Ostchega Y, Hales CM, Zhang G, Kruszon-Moran D. Hypertension prevalence and control among adults: United States, 2015-2016. NCHS Data Brief (2017) 289):1–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

