Alternative statistical modeling for radical prostatectomy data
- PMID: 38524792
- PMCID: PMC10956922
- DOI: 10.1080/02664763.2023.2229973
Alternative statistical modeling for radical prostatectomy data
Abstract
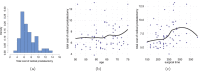
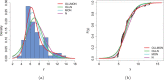
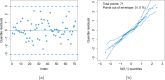
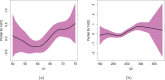
Several statistical models have been proposed in recent years, among them is the semiparametric regression. In medicine, there are several situations in which it is impracticable to consider a linear regression for statistical modeling, especially when the data contain explanatory variables that present a nonlinear relationship with the response variable. Another common situation is when the response variable does not have a unimodal shape, and it is not possible to adopt distributions belonging to the symmetric or asymmetric classes. In this context, a semiparametric heteroskedastic regression is proposed based on an extension of the normal distribution. Then, we show the usefulness of this model to analyze the cost of prostate cancer surgery. The predictor variables refer to two groups of patients such that one group receives a multimodal local anesthetic solution (Preemptive Target Anesthetic Solution) and the second group is treated with neuraxial blockade (spinal anesthesia/traditional standard). The other relevant predictor variables are also evaluated, thus allowing for the in-depth interpretation of the predictor variables with a nonlinear effect on the dependent variable cost. The penalized maximum likelihood method is adopted to estimate the model parameters. The new regression is a useful statistical tool for analyzing medical data.
Keywords: 62-08; 62-11; 62P10; Cubic smoothing splines; Marshall-Olkin family; local anesthetic; prostate cancer; quantile residuals.
© 2023 Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Atkinson A.C., Plots, Transformations and Regression; An Introduction to Graphical Methods of Diagnostic Regression Analysis, Clarendon Press Oxford, Oxford, 1985.
-
- Cardozo C.A., Paula G.A., and Venegas L.H., Generalized log-gamma additive partial linear models with P-spline smoothing, Stat. Papers 63 (2022), pp. 1953–1978.
-
- Chou R., Gordon D.B., de Leon-Casasola O.A., Rosenberg Ja.M., Bickler S., Brennan T., Carter. C.L. Cassidy T., Chittenden E.H., Degenhardt E., Griffith S., Manworren R., McCarberg B., Montgomery R., Murphy J., Perkal M.F., Suresh S., Sluka K., Strassels S., Thirlby R., Viscusi E., Walco G.A., Warner L., Weisman S.J., and Wu C.L., Management of postoperative pain: A clinical practice guideline from the American pain society, the American society of regional anesthesia and pain medicine, and the American society of anesthesiologists committee on regional anesthesia, executive committee, and administrative council, J. Pain 17 (2016), pp. 131–157. - PubMed
-
- da Silva Braga A., Cordeiro G.M., Ortega E.M., and da Cruz J.N., The odd log-logistic normal distribution: Theory and applications in analysis of experiments, J. Stat. Theory. Pract. 10 (2016), pp. 311–335.
-
- Dunn P.K. and Smyth G.K., Randomized quantile residuals, J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 5 (1996), pp. 236–244.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
