Scutellaria barbata D.Don extract regulates Ezrin-mediated triple negative breast cancer progress via suppressing the RhoA /ROCK1 signaling
- PMID: 38525246
- PMCID: PMC10958765
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfae033
Scutellaria barbata D.Don extract regulates Ezrin-mediated triple negative breast cancer progress via suppressing the RhoA /ROCK1 signaling
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) lacks effective therapeutic targets. Scutellaria barbata D.Don (SB) has been revealed to have anti-breast cancer (BC) effect, but the effect of SB extract in TNBC is still unclear. Herein, this research delves into the underlying mechanism.
Methods: SB was extracted by solvent extraction, and the main components were identified using an Agilent 6,520 HPLC-Chip/Q-TOF (Chip/Q-TOF) MS system. In vitro cell experiments were conducted. The effects of SB extract alone, SB extract plus EGF, GSK alone, GSK plus Ezrin overexpression, or SB extract plus Ezrin overexpression on cell viability, invasion, migration, and apoptosis were examined by cell function experiments. The apoptosis- and RhoA/ROCK1 pathway-related protein levels were analyzed by western blot assay.
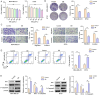
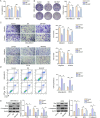
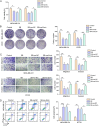
Results: Mass spectrometry analysis exhibited that SB extract mainly contains long-chain fatty acids and ursolic acid. SB extract mitigated TNBC cell biological phenotypes, apoptosis- and RhoA/ROCK1 pathway-related marker expressions, which were reversed by EGF. The further results found that GSK obviously weakens TNBC cell biological behaviors, apoptosis- and RhoA/ROCK1 signaling-related protein levels, while oe-Ezrin treatment reverses the effect of GSK on TNBC cells. Moreover, SB extract regulated Ezrin-mediated function of TNBC cells by impeding the RhoA/ROCK1 pathway.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrated that SB extract regulated Ezrin-mediated proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of TNBC cells via suppressing the RhoA /ROCK1 signaling. Our results offer the experimental foundation for further investigation of the anti-cancer role of SB in TNBC cells.
Highlights: SB extract inhibits the biological phenotypes of TNBC cells.SB extract inhibits the biological behaviors of TNBC cells through the RhoA/ROCK1 pathway.SB extract modulates Ezrin-mediated TNBC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis via restraining the RhoA/ROCK1 signaling.
Keywords: Ezrin; ROCK1; RhoA; scutellaria barbata D.Don extract; triple negative breast cancer.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Scutellaria barbata D.Don and Scleromitrion diffusum (Willd.) R.J.Wang inhibits the progression of triple negative breast cancer though the activation inhibition of NF-κB triggered by CAFs-derived IL6.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118656. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118656. Epub 2024 Aug 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39121924
-
Anti-tumor effect of Scutellaria barbata D. Don extracts on ovarian cancer and its phytochemicals characterisation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jul 12;206:184-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.05.032. Epub 2017 May 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28571726
-
Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of PI3K/AKT and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Dec;14(6):5527-5534. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5242. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29285087 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don exert antitumor activity in colorectal cancer through inhibited autophagy and promoted apoptosis via ATF4/sestrin2 pathway.Phytomedicine. 2022 May;99:154007. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154007. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35259610
-
Interaction Mechanisms Between the NOX4/ROS and RhoA/ROCK1 Signaling Pathways as New Anti- fibrosis Targets of Ursolic Acid in Hepatic Stellate Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2019 May 3;10:431. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00431. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31130857 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Triple-Negative HCC1937 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Revealed the Regulation of Migration and Invasion via the Downregulation of the Genes JAK2, ROCK1 and ROCK2.ACS Omega. 2025 Jul 9;10(28):31187-31200. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c05895. eCollection 2025 Jul 22. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40727786 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

