Neutrophil Percentage as a Potential Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury Risk and Short-Term Prognosis in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Elderly
- PMID: 38525316
- PMCID: PMC10959300
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S455588
Neutrophil Percentage as a Potential Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury Risk and Short-Term Prognosis in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Elderly
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the association of preoperative neutrophil percentage (NEUT%) with the risk of acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) having undergone coronary interventional therapy.
Methods: A single-center, retrospective and observational study was conducted. From December 2012 to June 2021, patients with AMI were enrolled and divided into AKI group and non-AKI group. The NEUT% in the two groups was compared. The association between NEUT% with the risk of post-AMI AKI was analyzed by univariate and multivariable logistic regression. Kaplan-Meier survival curve was drawn to evaluate the prognostic ability of NEUT% for short-term all-cause death following AMI.
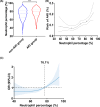
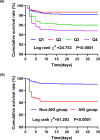
Results: A total of 3001 consecutive patients were enrolled with an average age of 64.38 years. AKI occurred in 327 (10.9%) patients. The NEUT% was higher in the AKI group than in the non-AKI group ([76.65±11.43]% versus [73.22±11.83]%, P<0.001). NEUT% was also identified as an independent risk factor for AKI in AMI patients after adjustment (OR=1.021, 95% CI: 1.010-1.033, P < 0.001). Compared with those at the lowest quartile of NEUT%, the patients at quartiles 2-4 had a higher risk of AKI (P for trend = 0.003). The odds of AKI increased by 29.0% as NEUT% increased by 1 standard deviation (OR=1.290, 95% CI: 1.087-1.531, P = 0.004). After a median of 35 days follow-up, 93 patients died. Patients with a higher NEUT% presented a higher risk of all-cause death after AMI (Log rank: χ2 =24.753, P<0.001).
Conclusion: In AMI patients, the peripheral blood NEUT% was positively associated with the odds of AKI and short-term all-cause mortality. NEUT% may provide physicians with more information about disease development and prognosis.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; acute myocardial infarction; neutrophil percentage.
© 2024 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effects of hemoglobin level on the risk of acute kidney injury in patients with acute myocardial infarction].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Dec;34(12):1243-1247. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20211113-01712. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 36567576 Chinese.
-
Stress hyperglycemia ratio as an independent predictor of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with acute myocardial infarction: a retrospective U.S. cohort study.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2471018. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2471018. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40012169 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor-15 levels and the risk of contrast induced acute kidney injury in acute myocardial infarction patients treated invasively: A propensity-score match analysis.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 12;13(3):e0194152. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194152. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29529072 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Incidence and the Prognostic Impact of Acute Kidney Injury in Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients: Current Preventive Strategies.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018 Feb;32(1):81-98. doi: 10.1007/s10557-017-6766-6. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2018. PMID: 29349645 Review.
-
Editor's Choice- What do small serum creatinine changes tell us about outcomes after acute myocardial infarction?Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2018 Dec;7(8):739-742. doi: 10.1177/2048872617728721. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2018. PMID: 28849947 Review.
Cited by
-
Sivelestat Sodium Alleviates Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Suppressing TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Mice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Oct 5;18:4449-4458. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S480148. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39399126 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil Percentage as a Potential Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury Risk and Short-term Prognosis in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Elderly [Response to Letter].Clin Interv Aging. 2024 May 15;19:843-844. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S477002. eCollection 2024. Clin Interv Aging. 2024. PMID: 38765793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Acute kidney injury after myocardial infarction: prognostic implications via dual robust methods.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 22;12:1555478. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1555478. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40766058 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil Percentage as a Potential Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury Risk and Short-Term Prognosis in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction in the Elderly [Letter].Clin Interv Aging. 2024 May 8;19:761-762. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S475956. eCollection 2024. Clin Interv Aging. 2024. PMID: 38736562 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Preoperative neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio as a postoperative AKI predictor in non-cardiac surgery: a retrospective cohort secondary analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 31;15(1):27994. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12949-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40745462 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

