Characterization of humoral and cellular immunologic responses to an mRNA-based human cytomegalovirus vaccine from a phase 1 trial of healthy adults
- PMID: 38526054
- PMCID: PMC11019844
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01603-23
Characterization of humoral and cellular immunologic responses to an mRNA-based human cytomegalovirus vaccine from a phase 1 trial of healthy adults
Abstract
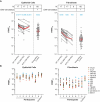
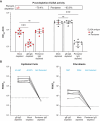
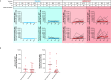
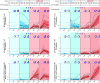
mRNA-1647 is an investigational mRNA-based vaccine against cytomegalovirus (CMV) that contains sequences encoding the CMV proteins glycoprotein B and pentamer. Humoral and cellular immune responses were evaluated in blood samples collected from healthy CMV-seropositive and CMV-seronegative adults who participated in a phase 1 trial of a three-dose series of mRNA-1647 (NCT03382405). Neutralizing antibody (nAb) titers against fibroblast and epithelial cell infection in sera from CMV-seronegative mRNA-1647 recipients were higher than those in sera from control CMV-seropositive samples and remained elevated up to 12 months after dose 3. nAb responses elicited by mRNA-1647 were comparable across 14 human CMV (HCMV) strains. Frequencies of antigen-specific memory B cells increased in CMV-seropositive and CMV-seronegative participants after each mRNA-1647 dose and remained elevated for up to 6 months after dose 3. mRNA-1647 elicited robust increases in frequencies and polyfunctionality of CD4+ T helper type 1 and effector CD8+ T cells in samples from CMV-seronegative and CMV-seropositive participants after stimulation with HCMV-specific peptides. The administration of three doses of mRNA-1647 to healthy adults elicited high nAb titers with wide-breadth, long-lasting memory B cells, and strong polyfunctional T-cell responses. These findings support further clinical development of the mRNA-1647 vaccine against CMV.IMPORTANCECytomegalovirus (CMV), a common virus that can infect people of all ages, may lead to serious health problems in unborn babies and those with a weakened immune system. Currently, there is no approved vaccine available to prevent CMV infection; however, the investigational messenger RNA (mRNA)-based CMV vaccine, mRNA-1647, is undergoing evaluation in clinical trials. The current analysis examined samples from a phase 1 trial of mRNA-1647 in healthy adults to better understand how the immune system reacts to vaccination. Three doses of mRNA-1647 produced a long-lasting immune response, thus supporting further investigation of the vaccine in the prevention of CMV infection.CLINICAL TRIALSRegistered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03382405).
Keywords: cytomegalovirus; immune response; messenger RNA; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of Moderna, Inc., and may hold stock/stock options in the company.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and Immunogenicity of a Messenger RNA-Based Cytomegalovirus Vaccine in Healthy Adults: Results From a Phase 1 Randomized Clinical Trial.J Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 23;230(3):e668-e678. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae114. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38478705 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Replication-Defective Human Cytomegalovirus Vaccine Elicits Humoral Immune Responses Analogous to Those with Natural Infection.J Virol. 2019 Nov 13;93(23):e00747-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00747-19. Print 2019 Dec 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31511385 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus mRNA-1647 Vaccine Candidate Elicits Potent and Broad Neutralization and Higher Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity Responses Than the gB/MF59 Vaccine.J Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 16;230(2):455-466. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad593. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38324766 Free PMC article.
-
The mRNA-1647 vaccine: A promising step toward the prevention of cytomegalovirus infection (CMV).Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2450045. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2450045. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 39825496 Review.
-
VCL-CB01, an injectable bivalent plasmid DNA vaccine for potential protection against CMV disease and infection.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2009 Oct;11(5):572-8. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19806506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progress and prospects of mRNA-based drugs in pre-clinical and clinical applications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Nov 14;9(1):322. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02002-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39543114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A vaccine against cytomegalovirus: how close are we?J Clin Invest. 2025 Jan 2;135(1):e182317. doi: 10.1172/JCI182317. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 39744948 Free PMC article.
-
Prophylactic and therapeutic vaccine development: advancements and challenges.Mol Biomed. 2024 Nov 11;5(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s43556-024-00222-x. Mol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 39527305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Autonomous Fusion Activity of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein B Is Regulated by Its Carboxy-Terminal Domain.Viruses. 2024 Sep 18;16(9):1482. doi: 10.3390/v16091482. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339958 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of human cytomegalovirus entry into mucosal epithelial cells.Antiviral Res. 2024 Oct;230:105971. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105971. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 39074588
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . 2020. Clinical overview. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/cmv/clinical/overview.html. Accessed 18 July 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

