Classification of early tuberculosis states to guide research for improved care and prevention: an international Delphi consensus exercise
- PMID: 38527485
- PMCID: PMC7616323
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(24)00028-6
Classification of early tuberculosis states to guide research for improved care and prevention: an international Delphi consensus exercise
Abstract
The current active-latent paradigm of tuberculosis largely neglects the documented spectrum of disease. Inconsistency with regard to definitions, terminology, and diagnostic criteria for different tuberculosis states has limited the progress in research and product development that are needed to achieve tuberculosis elimination. We aimed to develop a new framework of classification for tuberculosis that accommodates key disease states but is sufficiently simple to support pragmatic research and implementation. Through an international Delphi exercise that involved 71 participants representing a wide range of disciplines, sectors, income settings, and geographies, consensus was reached on a set of conceptual states, related terminology, and research gaps. The International Consensus for Early TB (ICE-TB) framework distinguishes disease from infection by the presence of macroscopic pathology and defines two subclinical and two clinical tuberculosis states on the basis of reported symptoms or signs of tuberculosis, further differentiated by likely infectiousness. The presence of viable Mycobacterium tuberculosis and an associated host response are prerequisites for all states of infection and disease. Our framework provides a clear direction for tuberculosis research, which will, in time, improve tuberculosis clinical care and elimination policies.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests AKC reports a grant (GNT2020750) from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. SMAZ reports personal support from the Commonwealth Scholarship Commission studentship. BWA reports funding for research, including salaries for group members, from the German Federal Ministry for Research and Education (BMBF). LM reports grant funding from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). DFW reports grants to his institution from NIH, the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the South African Medical Research Council, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, and the Research Council of Norway. RJW reports a grant to his institution from Wellcome. HE reports a grant (MR/V00476X/1) from the UK Medical Research Council and participation on a data safety monitoring board for the StatinTB trial. RMGJH reports a European Research Council Starting Grant (action number 757699). PKD, GG, MK, TK, BJM, GBM, MR, TJS, JAS, and PT declare no competing interests.
Figures
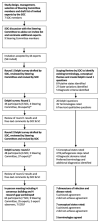
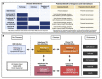
References
-
- Gothi GD. Natural History of Tuberculosis. Indian J Tuberc. 1978;25:13.
-
- National Tuberculosis Association. Diagnostic Standards and Classification of Tuberculosis. 1940 edition 1940.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

