Recent advances in the prevention and treatment of decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and the role of biomarkers
- PMID: 38527788
- PMCID: PMC11103292
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330584
Recent advances in the prevention and treatment of decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) and the role of biomarkers
Abstract
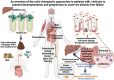
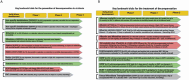
The progression of cirrhosis with clinically significant portal hypertension towards decompensated cirrhosis remains clinically challenging and the evolution towards acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF), with one or more extrahepatic organ failures, is associated with very high mortality. In the last decade, significant progress has been made in the understanding of the mechanisms leading to decompensation and ACLF. As portal hypertension advances, bacterial translocation across an impaired gut barrier culminates in endotoxaemia, systemic inflammation and cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction (CAID). Gut-derived systemic inflammation and CAID have become the logical targets for innovative therapies that prevent hepatic decompensation episodes and the progression to ACLF.Furthermore, classification of disease and biomarker discovery to personalise care have advanced in the field. This review discusses progress in biomarker discovery and personalisation of treatment in decompensated cirrhosis and ACLF.
Keywords: CIRRHOSIS; CLINICAL DECISION MAKING; LIVER FAILURE.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RH and ALG as an editor of the journal or an Editorial Board Member. JT has received speaking and/or consulting fees from Versantis, Gore, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Falk, Grifols, Genfit and CSL Behring.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
