Domperidone inhibits cell proliferation via targeting MEK and CDK4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38528618
- PMCID: PMC10964662
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03291-8
Domperidone inhibits cell proliferation via targeting MEK and CDK4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the leading causes of digestive system tumor related death in the world. Unfortunately, effective chemopreventive agent is lack for patients with ESCC in clinical practice, which leads to the extremely high mortality rate.
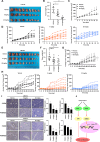
Methods: A library of prescribed drugs was screened for finding critical anti-tumor properties in ESCC cells. The phosphoproteomics, kinase array, pulldown assay and drug affinity responsive target stabilization assay (DARTS) were applied to explore mechanisms and searched for synergistic targets. Established models of PDX in mice were used to determine the therapeutic effect of domperidone.
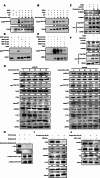
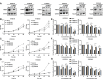
Results: After screening a library of prescribed drugs, we discovered that domperidone has anti-tumor properties. Domperidone, acting as a gastroprokinetic agent, has been widely used in clinic for gastrointestinal motility disorders. Despite limited research, there are indications that domperidone may have anti-tumor properties. In this study, we determined that domperidone significantly inhibited ESCC proliferation in vitro and in vivo. We employed phosphoproteomics to reveal p-ERK, and p-SMAD3 down-regulation upon domperidone treatment. Then, the results of kinase assay and pulldown assay further validated that domperidone directly combined with MEK1/2 and CDK4, leading to the inhibition of their kinase activity. Furthermore, our results revealed that MEK/ERK and CDK4/SMAD3 signal pathway were major pathways in domperidone against ESCC.
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings suggest that domperidone serves as an effective "multi-target" inhibitor of MEK1/2 and CDK4, offering potential benefits for the chemoprevention of ESCC.
Keywords: CDK4; Domperidone; ESCC; MEK1/2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Daurisoline suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo by targeting MEK1/2 kinase.Mol Carcinog. 2023 Apr;62(4):517-531. doi: 10.1002/mc.23503. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Mol Carcinog. 2023. PMID: 36645220
-
Azelnidipine inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation in vivo and in vitro by targeting MEK1/2.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022 Sep 26;27:61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.09.007. eCollection 2022 Dec 15. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022. PMID: 36284716 Free PMC article.
-
CDK4/6 inhibitor-SHR6390 exerts potent antitumor activity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting phosphorylated Rb and inducing G1 cell cycle arrest.J Transl Med. 2017 Jun 2;15(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1231-7. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28578693 Free PMC article.
-
Long non‑coding RNA BANCR promotes proliferation, invasion and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jun;23(6):465. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12104. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33880577 Free PMC article.
-
miR-1 suppresses the growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vivo and in vitro through the downregulation of MET, cyclin D1 and CDK4 expression.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Jul;38(1):113-22. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2619. Epub 2016 May 31. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27247259 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tanshinone IIA alleviates liver fibrosis by suppressing hepatic stellate cell proliferation via ERK/cyclin D1/p-Smad3L signaling axis.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025;28(5):638-646. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.83092.17962. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40666178 Free PMC article.
-
Domperidone inhibits dengue virus infection by targeting the viral envelope protein and nonstructural protein 1.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 30;15(1):3817. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87146-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39885306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cui Y, Chen H, Xi R, Cui H, Zhao Y, Xu E, Yan T, Lu X, Huang F, Kong P, et al. Whole-genome sequencing of 508 patients identifies key molecular features associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Res. 2020;30(10):902–13. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0333-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang ZX, Cui C, Yao J, Zhang Y, Li M, Feng J, Yang S, Fan Y, Shi J, Zhang X, et al. Toripalimab plus chemotherapy in treatment-naive, advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (JUPITER-06): a multi-center phase 3 trial. Cancer Cell. 2022;40(3):277–e288273. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.02.007. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 224200510015/Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Project
- 224200510015/Henan Province Science and Technology Innovation Talent Program
- 81872335/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81902486/National Outstanding Youth Science Fund Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

