World addiction medicine reports: formation of the International Society of Addiction Medicine Global Expert Network (ISAM-GEN) and its global surveys
- PMID: 38528974
- PMCID: PMC10961370
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1230318
World addiction medicine reports: formation of the International Society of Addiction Medicine Global Expert Network (ISAM-GEN) and its global surveys
Abstract
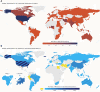
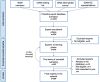
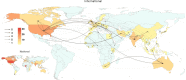
Addiction medicine is a dynamic field that encompasses clinical practice and research in the context of societal, economic, and cultural factors at the local, national, regional, and global levels. This field has evolved profoundly during the past decades in terms of scopes and activities with the contribution of addiction medicine scientists and professionals globally. The dynamic nature of drug addiction at the global level has resulted in a crucial need for developing an international collaborative network of addiction societies, treatment programs and experts to monitor emerging national, regional, and global concerns. This protocol paper presents methodological details of running longitudinal surveys at national, regional, and global levels through the Global Expert Network of the International Society of Addiction Medicine (ISAM-GEN). The initial formation of the network with a recruitment phase and a round of snowball sampling provided 354 experts from 78 countries across the globe. In addition, 43 national/regional addiction societies/associations are also included in the database. The surveys will be developed by global experts in addiction medicine on treatment services, service coverage, co-occurring disorders, treatment standards and barriers, emerging addictions and/or dynamic changes in treatment needs worldwide. Survey participants in categories of (1) addiction societies/associations, (2) addiction treatment programs, (3) addiction experts/clinicians and (4) related stakeholders will respond to these global longitudinal surveys. The results will be analyzed and cross-examined with available data and peer-reviewed for publication.
Keywords: addiction medicine; elicitation; expert; global; network; survey.
Copyright © 2024 Ekhtiari, Khojasteh Zonoozi, Rafei, Abolghasemi, Pemstein, Abdelgawad, Achab, Ghafri, Al’Absi, Bisch, Conti, Ambekar, Arunogiri, Bhad, Bilici, Brady, Bunt, Busse, Butner, Danesh, El-Khoury, Omari, Jokūbonis, Jong, Dom, Ebrahimi, Fathi Jouzdani, Ferri, Galea-Singer, Parker, Higuchi, Kathiresan, Khelifa, Kouimtsidis, Krupitsky, Long, Maremmani, McGovern, Mohaddes Ardabili, Rahimi-Movaghar, Rataemane, Sangchooli, Sibeko, Vella, Vista, Zare-Bidoky, Zhao, Javed, Potenza and Baldacchino.
Conflict of interest statement
2.10.6All the investigators involved in designing the surveys, analyzing the data, interpreting the results and publishing the reports will need to report any potential conflict of interest in advance and inform the principal investigators if there is any update in their conflict of interest within 3 months.Dr. MP has consulted for Opiant Therapeutics, Game Day Data, Baria-Tek, the Addiction Policy Forum, AXA, and Idorsia Pharmaceuticals; been involved in a patent application with Yale University and Novartis; received research support from Mohegan Sun Casino, Children and Screens and the Connecticut Council on Problem Gambling; is on the Boards of multiple organizations including the International Society of Addiction Medicine and the Addiction Policy Forum; been a principal investigator on a grant supporting the annual conference of the International Society of Addiction Medicine; participated in surveys, mailings, or telephone consultations related to drug addictions, internet use, impulse-control disorders, and other health topics; consulted for or advised gambling, non-profit and legal entities on issues related to internet use, impulse-control and/addictive disorders; and given academic lectures in grand rounds, continuing medical education events, and other clinical or scientific venues. Dr. AMB has no conflicts of interest with regard to the current work. However unrelated to this project he has received unrestricted educational grants from Schering Plough, Merck Serono, Reckitt Benckiser, CAMURUS and Indivior. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of commercial or financial relationships constituting conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lemahieu J-L, Me A. World Drug Report 2021. United Nations publication, Sales No. E.21.XI.8. Vienna, Austria: UNODC; (2021). Available at: https://www.unodc.org/res/wdr2021/field/WDR21_Booklet_2.pdf.
-
- Farhoudian A, Radfar SR, Mohaddes Ardabili H, Rafei P, Ebrahimi M, Khojasteh Zonoozi A, et al. A global survey on changes in the supply, price, and use of illicit drugs and alcohol, and related complications during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 1134. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.646206 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO/UNODC Substance use disorder treatment facility survey (2018). Available online at: https://www.unodc.org/documents/WHO_UNODC_Facility_survey_Draft_for_fiel....
-
- UNODC Documents . World Drug Report 2021 Methodological Annex. Vienna: Research and Trend Analysis Branch, UNODC; (2021).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

