Prognostic Value of Hemoglobin Concentration on Renal Outcomes with Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 38529168
- PMCID: PMC10962468
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S452280
Prognostic Value of Hemoglobin Concentration on Renal Outcomes with Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Objective: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) patients with anemia face an elevated risk of glomerular filtration rate decline. However, the association between hemoglobin and estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) progression remains to be elucidated.
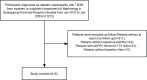
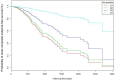
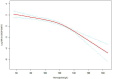
Methods: A retrospective cohort of 815 subjects with DKD was followed from January 2010 to January 2023. A Cox proportional hazard regression model was utilized to explore the predictive role of hemoglobin in renal outcomes. Renal outcomes were defined as a composite endpoint, including a 50% decline in eGFR from baseline or progression to End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD). To unveil any nonlinear relationship between hemoglobin and renal outcomes, Cox proportional hazard regression with cubic spline functions and smooth curve fitting was conducted. Additionally, subgroup analyses were performed to identify specific patient populations that might derive greater benefits from higher hemoglobin.
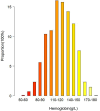
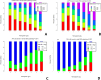
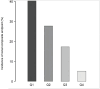
Results: Among the 815 DKD subjects, the mean age was 56.482 ± 9.924 years old, and 533 (65.4%) were male. The mean hemoglobin was 121.521±22.960 g/L. The median follow-up time was 21.103±18.335 months. A total of 182 (22.33%) individuals reached the renal composite endpoint during the study period. After adjusting for covariates, hemoglobin was found to exert a negative impact on the renal composite endpoint in patients with DKD (HR 0.975, 95% CI [0.966, 0.984]). A nonlinear relationship between hemoglobin and the renal composite endpoint was identified with an inflection point at 109 g/L. Subgroup analysis unveiled a more pronounced association between hemoglobin and renal prognosis in males.
Conclusion: Hemoglobin emerges as a predictive indicator for the renal prognosis of diabetic kidney disease in China. This study reveals a negative and non-linear relationship between hemoglobin levels and the renal composite endpoint. A substantial association is noted when hemoglobin surpasses 109 g/L in relation to the renal composite endpoint.
Keywords: Cox proportional-hazards regression; ESRD; diabetic kidney disease; eGFR decline; hemoglobin; non-linear.
© 2024 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Wysham CH, Gauthier-Loiselle M, Bailey RA, et al. Development of risk models for major adverse chronic renal outcomes among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using insurance claims: a retrospective observational study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2020;36(2):219–227. doi:10.1080/03007995.2019.1682981 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

