Beneficial role of amygdalin extracts against animal growth regulator Boldjan induced cardiac toxicity, injury and oxidative stress in male rats
- PMID: 38529199
- PMCID: PMC10960923
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfae042
Beneficial role of amygdalin extracts against animal growth regulator Boldjan induced cardiac toxicity, injury and oxidative stress in male rats
Abstract
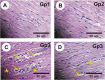
Millions of individuals have used illicit anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS), but the long-term cardiovascular associations of these drugs remain incompletely understood. Boldjan is AAS medication which is used in veterinary medicine and by young adults aiming to have a better appearance improving their self-esteem. Therefore; the objective of the current investigation was to examine any potential preventative effects of amygdalin extract against anabolic steroid Boldjan induced cardic toxicity, injury and oxidative stress in male rat. Forty adult male Wistar rats were classified into five groups (Gp1, Control Gp; Gp2, Amygdalin Gp in which rats treated with amygdalin (100 mg/kg body weight/day) daily for 2 weeks; Gp3, Boldjan Gp in which rats treated with Boldjan (10 mg/Kg BW/week) for 4 weeks; Gp4, Boldjan + Amygdalin). Boldjan induced a significant rises in serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine kinase (CK) and creatine kinase MB (CK MB), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), and very-low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (VLDL-C), cardiac injury, and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and a significant depletion in serum high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), cardiac reduced glutathione (GSH), Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (Cat) activities as compared to control Gp. In contrast, Amygdalin significantly reversed the Boldjan induced cardiac toxicity in post treated rats Gp (Boldjan + Amygdalin). Amygdalin could be an efficient preventive supplement for mitigating Boldjan induced cardiac toxicity, possibly via controlling oxidative stress events.
Keywords: Boldjan; amygdalin; anabolic-androgenic steroids; cardiac toxicity.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Tousson E, El-Moghazy M, El-Atrsh E. The possible effect of diets containing Nigella sativa and Thymus vulgaris on blood parameters and some organs structure in rabbit. Toxicol Ind Health. 2011:27(2):107–116. - PubMed
-
- Ayubi N, Kusnanik NW, Herawati L, Komaini A, Cholik T, Syafawi A. Abuse of anabolic-androgenic steroids and adverse effects on human organ health: a review. Biointerface Res Appl Chem. 2023:13(3):1–1.
-
- Tousson E, el-Moghazy M, Massoud A, Amani A. Histopathological and immunohistochemical changes in the testes of rabbits after injection with the growth promoter boldenone. Reprod Sci. 2012:19(3):253–259. - PubMed
-
- Tousson E, El-Moghazy M, Massoud A, El-Atrash A, Sweef O, Akel A. Physiological and biochemical changes after boldenone injection in adult rabbits. Toxicol Ind Health. 2016:32(1):177–182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

