EVA1A, a novel and promising prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 38529374
- PMCID: PMC10961441
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1333702
EVA1A, a novel and promising prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate the potential of EVA1A as a prognostic biomarker for Colorectal cancer (CRC).
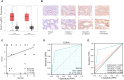
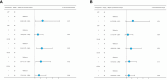
Methods: The study utilized public databases to analyze the difference in Evala mRNA expression between CRC tumor tissues and adjacent normal tissues. Additionallymunohistochemical staining was performed on 90 paired tissue samples to detect EVA1A expression. The relationship between EVA1A and clinicopathological features was examined, and a Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was conducted. Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were employed to identify prognostic factors affecting the overall survival (OS) of CRC patients.
Results: The analysis revealed a significant increase in Evala mRNA expression in CRC tumor cells compared to normal controls from public databases (P< 0.05). Immunohistochemical staining further confirmed a significant upregulation of EVA1A expression in CRC tissues (P< 0.05). High EVA1A expression was associated with age, pathological M stage, total tumor stage, and Carbohydrate antigen CA19-9 (CA19-9). Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated a significant association between high EVA1A expression and poor OS. Univariate and multivariate analysis identified EVA1A as an independent risk factor for CRC prognosis.
Conclusion: The study suggests that EVA1A is increased in CRC tumor tissues and may serve as a potential biomarker for poor prognosis in CRC.
Keywords: Eva-1 homolog A; biomarker; colorectal cancer; overall survival; prognosis.
Copyright © 2024 Fan and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

