This is a preprint.
Enrichment of Rare Variants of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Genes in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- PMID: 38529491
- PMCID: PMC10962746
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.03.13.24304215
Enrichment of Rare Variants of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Genes in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Update in
-
Enrichment of Rare Variants of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Genes in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024 Oct;76(10):1566-1572. doi: 10.1002/art.42938. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38937141 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate whether there is an enrichment of rare variants in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) genes and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) with or without macrophage activation syndrome (MAS).
Methods: Targeted sequencing of HLH genes (LYST, PRF1, RAB27A, STX11, STXBP2, UNC13D) was performed in sJIA subjects from an established cohort. Sequence data from control subjects were obtained in silico (dbGaP:phs000280.v8.p2). Rare variant association testing (RVT) was performed with sequence kernel association test (SKAT) package. Significance was defined as p<0.05 after 100,000 permutations.
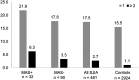
Results: Sequencing data from 524 sJIA cases were jointly called and harmonized with exome-derived target data from 3000 controls. Quality control operations produced a set of 481 cases and 2924 ancestrally-matched control subjects. RVT of sJIA cases and controls revealed a significant association with rare protein-altering variants (minor allele frequency [MAF]<0.01) of STXBP2 (p=0.020), and ultra-rare variants (MAF<0.001) of STXBP2 (p=0.007) and UNC13D (p=0.045). A subanalysis of 32 cases with known MAS and 90 without revealed significant association of rare UNC13D variants (p=0.0047). Additionally, sJIA patients more often carried ≥2 HLH variants than did controls (p=0.007), driven largely by digenic combinations involving LYST.
Conclusion: We identified an enrichment of rare HLH variants in sJIA patients compared with healthy controls, driven by STXBP2 and UNC13D. Biallelic variation in HLH genes was associated with sJIA, driven by LYST. Only UNC13D displayed enrichment in patients with MAS. This suggests that HLH variants may contribute to the pathophysiology of sJIA, even without MAS.
Figures

References
-
- Petty RE ST, Manners P, et al. International League of Associations for Rheumatology Classification of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Second Revision, Edmonton, 2001. The Journal of rheumatology. 2004;31(2):390–2. - PubMed
-
- Ravelli A, Minoia F, Davi S, et al. 2016 Classification Criteria for Macrophage Activation Syndrome Complicating Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology/Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation Collaborative Initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol. Mar 2016;68(3):566–76. doi: 10.1002/art.39332 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ombrello MJ, Arthur VL, Remmers EF, et al. Genetic architecture distinguishes systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis from other forms of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: clinical and therapeutic implications. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2016;doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210324 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
