Pharmacological suppression of the OTUD4/CD73 proteolytic axis revives antitumor immunity against immune-suppressive breast cancers
- PMID: 38530357
- PMCID: PMC11093616
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI176390
Pharmacological suppression of the OTUD4/CD73 proteolytic axis revives antitumor immunity against immune-suppressive breast cancers
Abstract
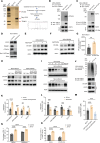
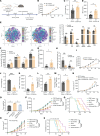
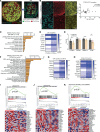
Despite widespread utilization of immunotherapy, treating immune-cold tumors remains a challenge. Multiomic analyses and experimental validation identified the OTUD4/CD73 proteolytic axis as a promising target in treating immune-suppressive triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Mechanistically, deubiquitylation of CD73 by OTUD4 counteracted its ubiquitylation by TRIM21, resulting in CD73 stabilization inhibiting tumor immune responses. We further demonstrated the importance of TGF-β signaling for orchestrating the OTUD4/CD73 proteolytic axis within tumor cells. Spatial transcriptomics profiling discovered spatially resolved features of interacting malignant and immune cells pertaining to expression levels of OTUD4 and CD73. In addition, ST80, a newly developed inhibitor, specifically disrupted proteolytic interaction between CD73 and OTUD4, leading to reinvigoration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cell activities. In preclinical models of TNBC, ST80 treatment sensitized refractory tumors to anti-PD-L1 therapy. Collectively, our findings uncover what we believe to be a novel strategy for targeting the immunosuppressive OTUD4/CD73 proteolytic axis in treating immune-suppressive breast cancers with the inhibitor ST80.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; Drug screens; Oncology; Therapeutics.
Figures




Comment in
- Posttranslational protein modifications as gatekeepers of cancer immunogenicity doi: 10.1172/JCI180914
References
-
- Song X, et al. Pharmacologic suppression of B7-H4 glycosylation restores antitumor immunity in immune-cold breast cancers. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(12):1872–1893. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA258765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK096990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA138292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA250110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA258857/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA202963/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA274620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM108569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM139297/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA250101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA217691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA222963/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA202948/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM012011/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

