Spatial patterning controls neuron numbers in the Drosophila visual system
- PMID: 38531357
- PMCID: PMC11078608
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.03.004
Spatial patterning controls neuron numbers in the Drosophila visual system
Abstract
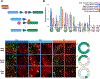
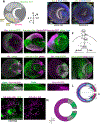
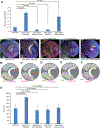
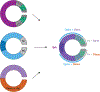
Neurons must be made in the correct proportions to communicate with the appropriate synaptic partners and form functional circuits. In the Drosophila visual system, multiple subtypes of distal medulla (Dm) inhibitory interneurons are made in distinct, reproducible numbers-from 5 to 800 per optic lobe. These neurons are born from a crescent-shaped neuroepithelium called the outer proliferation center (OPC), which can be subdivided into specific domains based on transcription factor and growth factor expression. We fate mapped Dm neurons and found that more abundant neural types are born from larger neuroepithelial subdomains, while less abundant subtypes are born from smaller ones. Additionally, morphogenetic Dpp/BMP signaling provides a second layer of patterning that subdivides the neuroepithelium into smaller domains to provide more granular control of cell proportions. Apoptosis appears to play a minor role in regulating Dm neuron abundance. This work describes an underappreciated mechanism for the regulation of neuronal stoichiometry.
Keywords: BMP signaling; Drosophila; cell number; neural development; optic lobe; spatial patterning.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Fischbach KF, and Dittrich APM (1989). The optic lobe of Drosophila melanogaster. I. A Golgi analysis of wild-type structure. Cell and Tissue Research 258, 441–475. 10.1007/BF00218858. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

