Long-term pasireotide therapy in acromegaly: extensive real-life experience of a referral center
- PMID: 38532073
- PMCID: PMC11266387
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-023-02299-7
Long-term pasireotide therapy in acromegaly: extensive real-life experience of a referral center
Abstract
Purpose: Pasireotide is a novel therapeutic option for patients with acromegaly resistant to first-generation somatostatin receptor ligands. To date, real-life data are still scant, therefore, the aim of the current study is to evaluate the impact of long-term pasireotide therapy on disease control, pituitary tumor size, gluco-insulinemic and lipid profile in a real-life setting.
Methods: Retrospective study of data prospectively collected, evaluating hormonal, tumoral, and metabolic data of 28 patients with acromegaly administered with pasireotide in a pituitary tertiary referral center.
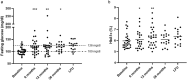
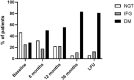
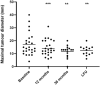
Results: Within the first 12 months of treatment, 70.4% of patients achieved normal IGF-I levels, which was maintained at 36-month evaluation in these responders patients. Patients who started with pasireotide 60 mg monthly exhibited significantly lower IGF-I levels after 36 months (p = 0.05) as compared to patients administered first with pasireotide 20 or 40 mg monthly. The maximal tumoral diameter was significantly decreased after 12 months of pasireotide (p < 0.001) and a further reduction was registered throughout the following months, with 41.2% of patients achieving a significant reduction (> 25% of baseline measurement) after 36 months of treatment. Fasting glucose significantly increased during the first 6 months (p < 0.001) with a gradual rise in diabetes prevalence during the following months, resulting diabetes prevalence after 36 months of pasireotide significantly increased compared to baseline (p = 0.003), although with glycated hemoglobin levels within the normal range. Diabetes was managed using oral glucose-lowering drugs or glucagon-like peptide 1 agonists, with no patient requiring insulin therapy. Pasireotide improved lipid profile, mainly during the first 12 months of treatment, by increasing HDL and decreasing triglycerides levels.
Conclusion: Pasireotide is effective and safe in the long-term. Hyperglycemia is a common event and is manageable even without insulin treatment.
Keywords: Acromegaly; Glucose; Insulin; Lipid; Pasireotide; Pituitary tumor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AC has been Principal Investigator of Research Studies for Novartis, Ipsen, Pfizer, Lilly, Merck and Novo Nordisk; consultant for Novartis, Ipsen, Pfizer, and received honoraria from Novartis, Ipsen and Pfizer beyond the confines of this work. RPiv has been Principal Investigator of Clinical and/or Translational Research Studies for Novartis, HRA Pharma, Ipsen, Shire, Corcept Therapeutics, Cortendo AB, Janssen Cilag, Camurus, Strongbridge, and Pfizer; Co-investigator of Research Studies for Pfizer; received research grants from Novartis, Pfizer, Ipsen, HRA Pharma, Shire, IBSA, Strongbridge Biopharma; has been an occasional consultant for Novartis, Ipsen, Pfizer, Shire, HRA Pharma, Cortendo AB, Ferring, Strongbridge Biopharma, Recordati, Corcept Therapeutics, Crinetics Pharmaceuticals, ARH Healthcare, Biohealth Italia, Italfarmaco; and has received fees and honoraria for presentations from Novartis, Shire, Pfizer and Recordati beyond the confines of this work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Effect of 6 Months' Treatment With Pasireotide LAR on Glucose Metabolism in Patients With Resistant Acromegaly in Real-World Clinical Settings.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 10;12:633944. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.633944. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33776927 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pasireotide on glucose- and growth hormone-related biomarkers in patients with inadequately controlled acromegaly.Endocrine. 2016 Jul;53(1):210-9. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0895-8. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Endocrine. 2016. PMID: 26906713 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The paradoxical GH response at OGTT does not predict Pasireotide efficacy but matters for glucose metabolism.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 May;48(5):1173-1183. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02534-3. Epub 2025 Jan 22. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 39841390 Free PMC article.
-
Pasireotide: a novel treatment for patients with acromegaly.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Jan 11;10:227-39. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S77999. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 26811671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Hyperglycemia in Patients With Acromegaly Treated With Pasireotide LAR.Drugs. 2016 Sep;76(13):1235-1243. doi: 10.1007/s40265-016-0615-y. Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27473537 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-world evidence of effectiveness and safety of pasireotide in the treatment of acromegaly: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2025 Feb;26(1):97-111. doi: 10.1007/s11154-024-09928-3. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 39527181 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of pasireotide on lipid and glucose metabolism in patients with acromegaly: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Jul 7. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02642-0. Online ahead of print. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 40622518 Review.
-
Differential Impact of Medical Therapies for Acromegaly on Glucose Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 8;26(2):465. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020465. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859181 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Colao A, Grasso LFS, Giustina A, Melmed S, Chanson P, Pereira AM, Pivonello R. (2019) Acromegaly. Nat Rev Dis Primers Mar 5 (1):20 - PubMed
-
- Giustina A, Barkhoudarian G, Beckers A, Ben-Shlomo A, Biermasz N, Biller B, Boguszewski C, Bolanowski M, Bollerslev J, Bonert V, Bronstein MD, Buchfelder M, Casanueva F, Chanson P, Clemmons D, Fleseriu M, Formenti AM, Freda P, Gadelha M, Geer E, Gurnell M, Heaney AP, Ho KKY, Ioachimescu AG, Lamberts S, Laws E, Losa M, Maffei P, Mamelak A, Mercado M, Molitch M, Mortini P, Pereira AM, Petersenn S, Post K, Puig-Domingo M, Salvatori R, Samson SL, Shimon I, Strasburger C, Swearingen B, Trainer P, Vance ML, Wass J, Wierman ME, Yuen KCJ, Zatelli MC, Melmed S (2020) Multidisciplinary management of acromegaly: A consensus. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 10.1007/s11154-020-09588-z 10.1007/s11154-020-09588-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colao A, Bronstein MD, Freda P, Gu F, Shen CC, Gadelha M, Fleseriu M, van der Lely AJ, Farrall AJ, Hermosillo Reséndiz K, Ruffin M, Chen Y, Sheppard M (2014) Pasireotide C2305 Study Group Pasireotide versus octreotide in acromegaly: a head-to-head superiority study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 10.1210/jc.2013-2480 10.1210/jc.2013-2480 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

