SIRT5 promote malignant advancement of chordoma by regulating the desuccinylation of c-myc
- PMID: 38532359
- PMCID: PMC10967166
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12140-w
SIRT5 promote malignant advancement of chordoma by regulating the desuccinylation of c-myc
Abstract
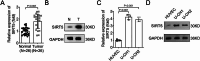
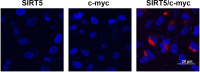
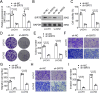
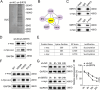
Chordoma is a relatively rare and locally aggressive malignant tumor. Sirtuin (SIRT)5 plays pivotal roles in various tumors, but the role of SIRT5 in chordoma has not been found. This study was performed to investigate the regulatory effects of SIRT5 on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and the underlying mechanism in chordoma. A xenograft tumor mouse model was established to assess tumor growth. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to analyze the mRNA levels of SIRT5 and c-myc. The effects of SIRT5 and c-myc on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of chordoma cells were detected by cell counting kit-8, colony formation, and Transwell assays. The interaction between SIRT5 and c-myc was evaluated by co-immunoprecipitation (IP) assay. The succinylation of c-myc was analyzed by IP and Western blot. The results showed that SIRT5 expression was upregulated in chordoma tissues and cells. SIRT5 interacted with c-myc to inhibit the succinylation of c-myc at K369 site in human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293T cells. Silencing of SIRT5 suppressed the cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of chordoma cells, while the results were reversed after c-myc overexpression. Moreover, silencing SIRT5 suppressed tumor growth in mice. These findings suggested that SIRT5 promoted the malignant advancement of chordoma by regulating the desuccinylation of c-myc.
Keywords: Chordoma; Desuccinylation; Migration; Proliferation; SIRT5; c-myc.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SIRT7 promotes the proliferation and migration of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells by regulating the desuccinylation of KIF23.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 15;24(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11965-9. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38360598 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT5 regulates granulosa cell proliferation and apoptosis in polycystic ovarian syndrome via desuccinylation of GLI1.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2025 Dec;41(1):2515516. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2025.2515516. Epub 2025 Jun 7. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40481676
-
SIRT5-mediated HOXA5 desuccinylation inhibits ferroptosis to alleviate sepsis induced-lung injury.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025 Jan;41(1):e12921. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12921. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39713961 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of mitochondrial sirtuin SIRT5 in succinylation modification and cancer development.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1531246. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1531246. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39944690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of the sirtuin deacylase SIRT5 in normal physiology and pathobiology.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Jun;53(3):311-334. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2018.1458071. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29637793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuin 5 inhibits mitochondrial metabolism in liver cancer cells and promotes apoptosis by mediating the desuccinylation of CS.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1560989. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1560989. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557149 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Cancer: A Revisited Review from Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies.Theranostics. 2024 May 11;14(7):2993-3013. doi: 10.7150/thno.97320. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38773972 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jo VY, Fletcher CD. WHO classification of soft tissue tumours: an update based on the 2013 (4th) edition. Pathology, 2014. 46(2): p. 95–104. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

