BMS-794833 reduces anlotinib resistance in osteosarcoma by targeting the VEGFR/Ras/CDK2 pathway
- PMID: 38532893
- PMCID: PMC10963651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbo.2024.100594
BMS-794833 reduces anlotinib resistance in osteosarcoma by targeting the VEGFR/Ras/CDK2 pathway
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma, a tumor that originates from bone cells, has a poor prognosis and a high degree of malignancy. Anlotinib, a small-molecule multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), is the first-line drug in treating osteosarcoma, especially in late-stage osteosarcoma. However, patients often develop resistance after using anlotinib for a certain period, which poses a challenge to its further clinical application. Recently, several TKIs, for instance regorafenib and cabozantinib, have showed clinical interest in treating osteosarcoma and target both vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and mesenchymal epithelial transition factor (c-MET). Therefore, the identification of new TKI warrants further investigation.
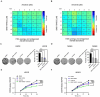
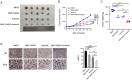
Methods: We performed CCK8 aasays to confirm that BMS-794833 sensitization osteosarcoma cells to anlotinib. Bioinformatics analysis and rescue experiments showed that the reduce of resistance were dependent on the VEGFR/Ras/CDK2 pathway. Cell line based xenograft model were used to demonstrate that BMS-794833 and anlotinib could synergistically treat OS.
Results: Here, we found that BMS-794833 reduced anlotinib resistance in osteosarcoma by targeting the VEGFR/Ras/CDK2 pathway. CCK8 assay showed that BMS-794833 significantly improved the resistance of osteosarcoma cells to anlotinib. The results of rescue experiments showed that the regulatory effects of BMS-794833 on the proliferation and drug resistance of osteosarcoma cells were dependent on the VEGFR/Ras/CDK2 pathway. In addition, BMS-794833 affected the resistance of osteosarcoma cells to anlotinib through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and apoptosis pathways. More importantly, BMS-794833 and anlotinib exerted synergistic therapeutic effects against osteosarcoma in vivo.
Conclusion: Altogether, this study reveals a new (VEGFR)-targeting drug that can be combined with anlotinib for the treatment of osteosarcoma, which provides an important theoretical basis for overcoming anlotinib resistance.
Keywords: Anlotinib; CDK2; Osteosarcoma; Synergy effect; VEGFR.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tocilizumab (monoclonal anti-IL-6R antibody) reverses anlotinib resistance in osteosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 19;13:1192472. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1192472. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37404767 Free PMC article.
-
Anlotinib, a novel small molecular tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses growth and metastasis via dual blockade of VEGFR2 and MET in osteosarcoma.Int J Cancer. 2019 Aug 15;145(4):979-993. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32180. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30719715
-
PI3K inhibitor impairs tumor progression and enhances sensitivity to anlotinib in anlotinib-resistant osteosarcoma.Cancer Lett. 2022 Jun 28;536:215660. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215660. Epub 2022 Mar 19. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35318116
-
Effective treatment of anlotinib in giant delayed pulmonary metastasis of osteosarcoma: a case report and literature review.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jun;10(6):7073-7082. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1790. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 33548989 Review.
-
Anlotinib: a novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Sep 19;11(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0664-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30231931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Patient-derived rhabdomyosarcoma cells recapitulate the genetic and transcriptomic landscapes of primary tumors.iScience. 2024 Aug 31;27(10):110862. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110862. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39319271 Free PMC article.
-
The role and research progress of the MET signalling pathway in targeted therapy for osteosarcoma.Oncol Rev. 2025 Jun 17;19:1615111. doi: 10.3389/or.2025.1615111. eCollection 2025. Oncol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40599602 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beird H.C., Bielack S.S., Flanagan A.M., Gill J., Heymann D., Janeway K.A., Livingston J.A., Roberts R.D., Strauss S.J., Gorlick R. Osteosarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2022;8(1):77. - PubMed
-
- Liu X.Y., Li M., Dong B., Feng Q. Caprin1 targeted by circular circ_0000885 in the tumor progression of osteosarcoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020;24(17):8631. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

