Sub-segmental pulmonary thromboembolism in a pregnant woman with generalized lupus erythematosus, triple-negative antiphospholipid syndrome, and protein C deficiency. A case report
- PMID: 38532907
- PMCID: PMC10963187
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.02.065
Sub-segmental pulmonary thromboembolism in a pregnant woman with generalized lupus erythematosus, triple-negative antiphospholipid syndrome, and protein C deficiency. A case report
Abstract
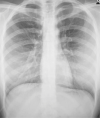
Autoimmune diseases and thrombophilic disorders, notably antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and protein S deficiency, present a formidable challenge in pregnancy, substantially increasing the risk of thromboembolic complications by up to 20%. Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE), characterized by a significantly higher maternal mortality rate, is of particular concern. APS, defined by the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, emerges as a pivotal risk factor for PTE during pregnancy, especially in women exhibiting triple negativity. Concurrently, protein S deficiency further amplifies vulnerability to thromboembolic events, establishing a high-risk scenario for pregnant individuals. In a case involving a 29-year-old pregnant woman with a history of generalized lupus erythematosus, triple-negative antiphospholipid syndrome, and protein S deficiency, sudden-onset dyspnea prompted thorough investigation. Despite her complex medical history, a multidisciplinary approach led to the accurate diagnosis and successful management of subsegmental pulmonary thromboembolism, ensuring the well-being of both mother and fetus. Effectively managing PTE during pregnancy demands a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach involving collaboration among obstetricians, internists, rheumatologists, and hematologists. Accurate diagnosis, tailored anticoagulation strategies, and continuous monitoring stand as indispensable pillars for maternal and fetal well-being.
Keywords: Antiphospholipid síndrome; Pregnancy complications; Protein S deficiency; Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE); Thrombophilic disorders.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Alijotas-Reig J, Esteve-Valverde E, Ferrer-Oliveras R, Sáez-Comet L, Lefkou E, Mekinian A, et al. The European Registry on Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome (EUROAPS): a survey of 1000 consecutive cases. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18(4):406–414. - PubMed
-
- Rodger MA, Carrier M, Le Gal G, Martinelli I, Perna A, Rey E, et al. Meta-analysis of low-molecular-weight heparin to prevent recurrent placenta-mediated pregnancy complications. Blood. 2014;123(6):822–828. - PubMed
-
- Lippi G. An update on common inherited thrombophilic conditions. Clin Res Commun. 2023;6(4):22.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

