Keto Clarity: A Comprehensive Systematic Review Exploring the Efficacy, Safety, and Mechanisms of Ketogenic Diet in Pediatric Epilepsy
- PMID: 38533170
- PMCID: PMC10964213
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.54863
Keto Clarity: A Comprehensive Systematic Review Exploring the Efficacy, Safety, and Mechanisms of Ketogenic Diet in Pediatric Epilepsy
Abstract
Epilepsy, a widespread neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, affects millions globally, with a significant impact on the pediatric population. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) constitute the primary treatment; however, drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE), especially in children, poses a therapeutic challenge. Alternative interventions, such as surgery, vagus nerve stimulation, and the ketogenic diet (KD), have been explored. This systematic review aims to investigate various types of KDs, their distinctions, their effectiveness, and their safety concerning the reduction of seizure frequency, achieving seizure freedom, and the occurrence of adverse events. The study adheres to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. A comprehensive search was conducted using databases such as PubMed Central (PMC), MedLine, and Science Direct to identify relevant articles. Eligibility criteria and quality assessment tools were applied to evaluate the potential risk of bias and select 11 articles for inclusion in this review. The selected articles encompassed four randomized controlled trials (RCTs), two systematic reviews, and five narrative reviews. The data collected for this review was completed on October 2, 2023. Challenges, such as palatability, cultural factors, and adherence difficulties, were identified. Family or caregiver involvement plays a pivotal role in treatment success. Despite numerous RCTs and reviews, information gaps persist, hindering conclusive outcomes. Evaluating the risk-benefit ratio is crucial, considering potential side effects. The highly individualized nature of KD therapy, influenced by diverse seizure types and syndromes, necessitates a trial-and-error approach monitored by a multidisciplinary team. Long-term safety and efficacy demand continuous real-life patient data review. In summary, while KD presents a promising alternative for DRE, its success relies on meticulous planning, individualized implementation, and ongoing research to address existing challenges and information gaps.
Keywords: classic ketogenic diet; drug-resistant epilepsy (dre); epilepsy; ketogenic diet; low glycemic index treatment (lgit); medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diet (mctkd); modified atkins diet (mad); pediatric neurology; pediatrics; seizure.
Copyright © 2024, Faheem et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
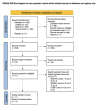
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and compliance of carbohydrate-restricted diets for treating drug-resistant epilepsy: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Epilepsy Behav. 2025 Jul;168:110434. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2025.110434. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Epilepsy Behav. 2025. PMID: 40252525
-
The impact of ketogenic diet on drug-resistant epilepsy in children: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Jun;193(3):1495-1503. doi: 10.1007/s11845-024-03622-8. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38315271 Review.
-
Efficacy of Ketogenic Diet, Modified Atkins Diet, and Low Glycemic Index Therapy Diet Among Children With Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Pediatr. 2020 Oct 1;174(10):944-951. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.2282. JAMA Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32761191 Free PMC article.
-
Illuminating the Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Different Ketogenic Diets for Individuals with Epilepsy: A Scoping Meta-Review.Seizure. 2025 Feb;125:140-151. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2025.01.018. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Seizure. 2025. PMID: 39842187
-
Effect of the ketogenic diet as a treatment for refractory epilepsy in children and adolescents: a systematic review of reviews.Nutr Rev. 2024 Mar 11;82(4):487-502. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad071. Nutr Rev. 2024. PMID: 37400987
Cited by
-
Ketogenic diets in clinical psychology: examining the evidence and implications for practice.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1468894. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1468894. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39391844 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Safety and tolerability of the ketogenic diet used for the treatment of refractory childhood epilepsy: a systematic review of published prospective studies. Cai QY, Zhou ZJ, Luo R, Gan J, Li SP, Mu DZ, Wan CM. World J Pediatr. 2017;13:528–536. - PubMed
-
- The place of a ketogenic diet in the treatment of resistant epilepsy: a comprehensive review. Cicek E, Sanlier N. Nutr Neurosci. 2023;26:828–841. - PubMed
-
- The ketogenic diet--update on recent clinical trials. Cross JH, Neal EG. Epilepsia. 2008;49:6–10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources