Naodesheng decoction regulating vascular function via G-protein-coupled receptors: network analysis and experimental investigations
- PMID: 38533257
- PMCID: PMC10963398
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1355169
Naodesheng decoction regulating vascular function via G-protein-coupled receptors: network analysis and experimental investigations
Abstract
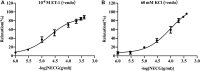
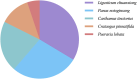
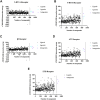
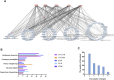
Introduction: Ischemic stroke (IS) is a detrimental neurological disease with limited treatment options. Recanalization of blocked blood vessels and restoring blood supply to ischemic brain tissue are crucial for post-stroke rehabilitation. The decoction Naodesheng (NDS) composed of five Chinese botanical drugs, including Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F. H. Chen, Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort., Carthamus tinctorius L., Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi, and Crataegus pinnatifida Bge., is a blood-activating and stasis-removing herbal medicine commonly used for the clinical treatment of cerebrovascular diseases in China. However, the material basis of NDS on the effects of blood circulation improvement and vascular tone regulation remains unclear. Methods: A database comprising 777 chemical metabolites of NDS was constructed. Then, the interactions between various herbal metabolites of NDS and five vascular tone modulation G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), including 5-HT1AR, 5-HT1BR, β2-AR, AT1R, and ETBR, were assessed by molecular docking. Using network analysis and vasomotor experiment of the cerebral basilar artery, the potential material basis underlying the vascular regulatory effects of NDS was further explored. Results: The Naodesheng Effective Component Group (NECG) was found to induce relaxation of rat basilar artery rings precontracted using Endothelin-1 (ET-1) and KCl in vitro in a dose-dependent manner. Several metabolites of NDS, including C. tinctorius, C. pinnatifida, and P. notoginseng, were found to be the main plant resources of metabolites with high docking scores. Furthermore, several metabolites in NDS, including formononetin-7-glucoside, hydroxybenzoyl-coumaric anhydride, methoxymecambridine, puerarol, and pyrethrin II, were found to target multiple vascular GPCRs. Metabolites with moderate-to-high binding energy were verified to have good rat basilar artery-relaxing effects, and the maximum artery relaxation effects of all three metabolites, namely, isorhamnetin, kaempferol, and daidzein, were found to exceed 90%. Moreover, metabolites of NDS were found to exert a synergistic effect by interacting with vascular GPCR targets, and these metabolites may contribute to the cerebrovascular regulatory function of NDS. Discussion: The study reports that various metabolites of NDS contribute to its vascular tone regulating effects and demonstrates the multi-component and multi-target characteristics of NDS. Among them, metabolites with moderate-to-high binding scores in NDS may play an important role in regulating vascular function.
Keywords: G-protein-coupled receptor; Naodesheng decoction; material basis; molecular docking; network analysis; vascular function.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Niu, Shen, Lu, Zhao, Yang, Guo, Zhang, Zheng, Du and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Xiaoxuming Decoction Regulates Vascular Function by Modulating G Protein-Coupled Receptors: A Molecular Docking Study.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jun 5;2021:5575443. doi: 10.1155/2021/5575443. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34195269 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology-based analysis of Chinese herbal Naodesheng formula for application to Alzheimer's disease.Chin J Nat Med. 2018 Jan;16(1):53-62. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(18)30029-3. Chin J Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 29425590
-
Effects of Naodesheng tablets on amyloid beta-induced dysfunction: A traditional Chinese herbal formula with novel therapeutic potential in Alzheimer's disease revealed by systems pharmacology.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Sep;141:111916. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111916. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34328103
-
Effect of Panax notoginseng Saponins on Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rat Models: A Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 9;11:572304. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.572304. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33643030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jul 21;188:234-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27154405 Review.
References
-
- Bobe G., Albert P. S., Sansbury L. B., Lanza E., Schatzkin A., Colburn N. H., et al. (2010). Interleukin-6 as a potential indicator for prevention of high-risk adenoma recurrence by dietary flavonols in the polyp prevention trial. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 3 (6), 764–775. 10.1158/1940-6207.Capr-09-0161 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

