Redirecting pantoprazole as a metallo-beta-lactamase inhibitor in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 38533260
- PMCID: PMC10963397
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1366459
Redirecting pantoprazole as a metallo-beta-lactamase inhibitor in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
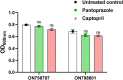
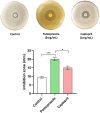
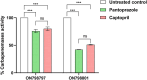
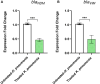
The development of resistance to carbapenems in Klebsiella pneumoniae due to the production of metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) is a critical public health problem because carbapenems are the last-resort drugs used for treating severe infections of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) producing K. pneumoniae. Restoring the activity of carbapenems by the inhibition of metallo-β-lactamases is a valuable approach to combat carbapenem resistance. In this study, two well-characterized clinical multidrug and carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae isolates were used. The sub-inhibitory concentrations of pantoprazole and the well-reported metallo-β-lactamase inhibitor captopril inhibited the hydrolytic activities of metallo-β-lactamases, with pantoprazole having more inhibiting activities. Both drugs, when used in combination with meropenem, exhibited synergistic activities. Pantoprazole could also downregulate the expression of the metallo-β-lactamase genes bla NDM and bla VIM. A docking study revealed that pantoprazole could bind to and chelate zinc ions of New Delhi and Verona integron-encoded MBL (VIM) enzymes with higher affinity than the control drug captopril and with comparable affinity to the natural ligand meropenem, indicating the significant inhibitory activity of pantoprazole against metallo-β-lactamases. In conclusion, pantoprazole can be used in combination with meropenem as a new strategy for treating serious infections caused by metallo-β-lactamases producing K. pneumoniae.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; carbapenems; healthcare; metallo-β-lactamase inhibitor; pantoprazole.
Copyright © 2024 Abdulaal, Alhakamy, Asseri, Radwan, Ibrahim, Okbazghi, Abbas, Mansour, Shoun, Hegazy and Abdel-Halim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sulfamoyl Heteroarylcarboxylic Acids as Promising Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibitors for Controlling Bacterial Carbapenem Resistance.mBio. 2020 Mar 17;11(2):e03144-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03144-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32184250 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Development of a β-Lactam-Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibitor: Targeting Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales.ACS Infect Dis. 2023 Mar 10;9(3):486-496. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00485. Epub 2023 Feb 14. ACS Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36786013 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of specific inhibitors on metallo-β-carbapenemases detected in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jul;132:266-274. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.05.022. Epub 2019 May 13. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31096002
-
Epidemiology and Characteristics of Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Infect Chemother. 2015 Jun;47(2):81-97. doi: 10.3947/ic.2015.47.2.81. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Infect Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26157586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30712199 Review.
Cited by
-
Reviving Furosemide as a Metallo-β-Lactamase Inhibitor against MDR Acinetobacter baumannii.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 7;35:e2506023. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2506.06023. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40774820 Free PMC article.
-
Encoding Genes of Metallo β-Lactamases (IMP, NDM, and VIM) in Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 18;8(6):e70927. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70927. eCollection 2025 Jun. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40535515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical profile, virtual screening, and virulence-inhibiting properties of Sphagneticola trilobata L. essential oils against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 8;15(1):11964. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94486-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40199892 Free PMC article.
-
Reprofiling lamivudine as an antibiofilm and anti-pathogenic agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.AMB Express. 2025 Feb 22;15(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13568-025-01835-3. AMB Express. 2025. PMID: 39985628 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in Klebsiella: Advances in Detection Methods and Clinical Implications.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Mar 11;18:1339-1354. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S509016. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40092844 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akajagbor D. S., Wilson S. L., Shere-Wolfe K. D., Dakum P., Charurat M. E., Gilliam B. L. (2013). Higher incidence of acute kidney injury with intravenous colistimethate sodium compared with polymyxin B in critically ill patients at a tertiary care medical center. Clin. Infect. Dis. 57, 1300–1303. 10.1093/cid/cit453 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

