Effects of online tDCS and hf-tRNS on reading performance in children and adolescents with developmental dyslexia: a study protocol for a cross sectional, within-subject, randomized, double-blind, and sham-controlled trial
- PMID: 38533416
- PMCID: PMC10964771
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1338430
Effects of online tDCS and hf-tRNS on reading performance in children and adolescents with developmental dyslexia: a study protocol for a cross sectional, within-subject, randomized, double-blind, and sham-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Developmental Dyslexia (DD) is a brain-based developmental disorder causing severe reading difficulties. The extensive data on the neurobiology of DD have increased interest in brain-directed approaches, such as transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which have been proposed for DD. While positive outcomes have been observed, results remain heterogeneous. Various methodological approaches have been employed to address this issue. However, no studies have compared the effects of different transcranial electrical stimulation techniques (e.g., tDCS and transcranial random noise stimulation, tRNS), on reading in children and adolescents with DD.
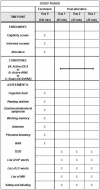
Methods: The present within-subject, double-blind, and sham-controlled trial aims to investigate the effects of tDCS and hf-tRNS on reading in children and adolescents with DD. Participants will undergo three conditions with a one-week interval session: (A) single active tDCS session; (B) single active hf-tRNS session; and (C) single sham session (tDCS/hf-tRNS). Left anodal/right cathodal tDCS and bilateral tRNS will be applied over the temporo-parietal regions for 20 min each. Reading measures will be collected before and during each session. Safety and blinding parameters will be recordered.
Discussion: We hypothesize that tRNS will demonstrate comparable effectiveness to tDCS in improving reading compared to sham conditions. Additionally, we anticipate that hf-tRNS will exhibit a similar safety profile to tDCS. This study will contribute novel insights into the effectiveness of hf-tRNS, expediting the validation of brain-based treatments for DD.
Keywords: brain stimulation; learning disorders; neurodevelopmental disorders; tES; treatment.
Copyright © 2024 Battisti, Lazzaro, Varuzza, Vicari and Menghini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer AC declared a shared affiliation with the author SV to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of a short, intensive, multi-session tDCS treatment in developmental dyslexia: Preliminary results of a sham-controlled randomized clinical trial.Prog Brain Res. 2021;264:191-210. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2021.01.015. Prog Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 34167656 Clinical Trial.
-
Examining transcranial random noise stimulation as an add-on treatment for persistent symptoms in schizophrenia (STIM'Zo): a study protocol for a multicentre, double-blind, randomized sham-controlled clinical trial.Trials. 2021 Dec 28;22(1):964. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05928-9. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34963486 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a short and intensive transcranial direct current stimulation treatment in children and adolescents with developmental dyslexia: A crossover clinical trial.Front Psychol. 2022 Sep 9;13:986242. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.986242. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36160506 Free PMC article.
-
tDCS Modulatory Effect on Reading Processes: A Review of Studies on Typical Readers and Individuals With Dyslexia.Front Behav Neurosci. 2018 Jul 31;12:162. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00162. eCollection 2018. Front Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30108491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the Effects of Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation Techniques on Developmental Dyslexia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Iran J Psychiatry. 2025 Apr;20(2):209-222. doi: 10.18502/ijps.v20i2.18203. Iran J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40521277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Detecting the contribution of V5/MT in reading, reading-related tasks, eye-movements and EEG-oscillations in children and adolescents with developmental dyslexia via high-definition tDCS: a protocol study.BMC Psychol. 2025 Jul 7;13(1):744. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-03036-w. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40624571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Association; (2013). 947 p.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

