The Extended Chest Wall Perforator Flap: Expanding the Indication for Partial Breast Reconstruction
- PMID: 38533519
- PMCID: PMC10965203
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005697
The Extended Chest Wall Perforator Flap: Expanding the Indication for Partial Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
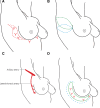
Background: The intercostal artery perforator flap has traditionally been used to reconstruct small or moderate-sized single defects in the lateral or lower medial breast during breast-conserving surgery. We report a modification of the intercostal artery perforator flap that allows for reconstruction of larger breast tumors than previously described flap designs.
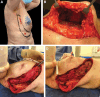
Methods: A retrospective study of breast cancer patients undergoing breast-conserving surgery and immediate partial breast reconstruction with an extended chest wall perforator flap. Primary outcomes were successful tumor excision, adequate radial margins, postoperative complications, and delays to adjuvant radiotherapy.
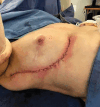
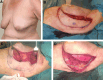
Results: Thirty patients were included. Mean radiological tumor size was 27 mm (11-56 mm) and excision volume, 123 cm3 (18-255 cm3). All tumors had satisfactory excision margins, and no patient required further surgery for re-excision. In the early postoperative period, one patient required radiological drainage of seroma, and one returned to theater for debridement of fat necrosis affecting the flap. Ten other patients were managed on an outpatient basis for minor wound complications. All patients were followed up annually for 5 years. No patients had a delay to adjuvant treatment or required revisional procedures for cosmesis.
Conclusions: The modified chest wall perforator flap allows for breast conservation for larger tumors from all quadrants of the breast, including centrally located tumors and reconstruction of the axillary defect following lymph node clearance. The length of the flap allows for the use of multiple perforators in the pedicle area and freedom of the flap to reach the defects. This can be performed with low morbidity and no delay to adjuvant radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, et al. . Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1233–1241. - PubMed
-
- Breast Cancer Care. Breast cancer the numbers. Available at https://breastcancernow.org/sites/default/files/files/breast-cancer-stat.... Published 2015. Accessed February 13, 2023.
-
- Mohamedahmed AYY, Zaman S, Zafar S, et al. . Comparison of surgical and oncological outcomes between oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery versus conventional breast-conserving surgery for treatment of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 31 studies. Surg Oncol. 2022;42:101779. - PubMed
-
- Down SK, Jha PK, Burger A, et al. . Oncological advantages of oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery in treatment of early breast cancer. Breast J. 2013;19:56–63. - PubMed
-
- Hamdi M, Van Landuyt K, Monstrey S, et al. . Pedicled perforator flaps in breast reconstruction: a new concept. Br J Plast Surg. 2004;57:531–539. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
