Inter-plane feedback coordinates cell morphogenesis and maintains 3D tissue organization in the Drosophila pupal retina
- PMID: 38533736
- PMCID: PMC11006395
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.201757
Inter-plane feedback coordinates cell morphogenesis and maintains 3D tissue organization in the Drosophila pupal retina
Abstract
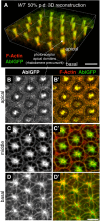
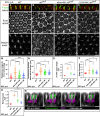
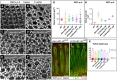
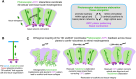
How complex organs coordinate cellular morphogenetic events to achieve three-dimensional (3D) form is a central question in development. The question is uniquely tractable in the late Drosophila pupal retina, where cells maintain stereotyped contacts as they elaborate the specialized cytoskeletal structures that pattern the apical, basal and longitudinal planes of the epithelium. In this study, we combined cell type-specific genetic manipulation of the cytoskeletal regulator Abelson (Abl) with 3D imaging to explore how the distinct cellular morphogenetic programs of photoreceptors and interommatidial pigment cells (IOPCs) organize tissue pattern to support retinal integrity. Our experiments show that photoreceptor and IOPC terminal differentiation is unexpectedly interdependent, connected by an intercellular feedback mechanism that coordinates and promotes morphogenetic change across orthogonal tissue planes to ensure correct 3D retinal pattern. We propose that genetic regulation of specialized cellular differentiation programs combined with inter-plane mechanical feedback confers spatial coordination to achieve robust 3D tissue morphogenesis.
Keywords: Drosophila eye development; 3D cytoskeletal network; Abelson; Actin cytoskeleton; Apical–basal polarity; Cell–cell interactions; Epithelial patterning; Feedback mechanism; Morphogenesis; Photoreceptor; Pigment cell.
© 2024. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Orthogonal coupling of a 3D cytoskeletal scaffold coordinates cell morphogenesis and maintains tissue organization in the Drosophila pupal retina.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 7:2023.03.06.531386. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.06.531386. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Development. 2024 Mar 15;151(6):dev201757. doi: 10.1242/dev.201757. PMID: 36945525 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

