vNARs as Neutralizing Intracellular Therapeutic Agents: Glioblastoma as a Target
- PMID: 38534215
- PMCID: PMC10967338
- DOI: 10.3390/antib13010025
vNARs as Neutralizing Intracellular Therapeutic Agents: Glioblastoma as a Target
Abstract
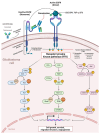
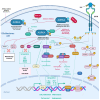
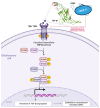
Glioblastoma is the most prevalent and fatal form of primary brain tumors. New targeted therapeutic strategies for this type of tumor are imperative given the dire prognosis for glioblastoma patients and the poor results of current multimodal therapy. Previously reported drawbacks of antibody-based therapeutics include the inability to translocate across the blood-brain barrier and reach intracellular targets due to their molecular weight. These disadvantages translate into poor target neutralization and cancer maintenance. Unlike conventional antibodies, vNARs can permeate tissues and recognize conformational or cryptic epitopes due to their stability, CDR3 amino acid sequence, and smaller molecular weight. Thus, vNARs represent a potential antibody format to use as intrabodies or soluble immunocarriers. This review comprehensively summarizes key intracellular pathways in glioblastoma cells that induce proliferation, progression, and cancer survival to determine a new potential targeted glioblastoma therapy based on previously reported vNARs. The results seek to support the next application of vNARs as single-domain antibody drug-conjugated therapies, which could overcome the disadvantages of conventional monoclonal antibodies and provide an innovative approach for glioblastoma treatment.
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy; glioblastoma; intrabodies; molecular targeted therapy; receptor tyrosine kinase; variable new antigen receptors (vNARs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ostrom Q.T., Gittleman H., Liao P., Rouse C., Chen Y., Dowling J., Wolinsky Y., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16:iv1–iv63. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou223. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

