Recent Research Trends in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Disorders
- PMID: 38534355
- PMCID: PMC10969521
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13060511
Recent Research Trends in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Disorders
Abstract
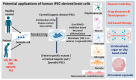
Neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), traumatic brain injury (TBI) and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) are chronic major health disorders. The exact mechanism of the neuroimmune dysfunctions of these disease pathogeneses is currently not clearly understood. These disorders show dysregulated neuroimmune and inflammatory responses, including activation of neurons, glial cells, and neurovascular unit damage associated with excessive release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, neurotoxic mediators, and infiltration of peripheral immune cells into the brain, as well as entry of inflammatory mediators through damaged neurovascular endothelial cells, blood-brain barrier and tight junction proteins. Activation of glial cells and immune cells leads to the release of many inflammatory and neurotoxic molecules that cause neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Gulf War Illness (GWI) and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) are chronic disorders that are also associated with neuroimmune dysfunctions. Currently, there are no effective disease-modifying therapeutic options available for these diseases. Human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived neurons, astrocytes, microglia, endothelial cells and pericytes are currently used for many disease models for drug discovery. This review highlights certain recent trends in neuroinflammatory responses and iPSC-derived brain cell applications in neuroinflammatory disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Gulf War Illness; Parkinson’s disease; human induced pluripotent stem cells; myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome; neuroinflammation; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pathak N., Vimal S.K., Tandon I., Agrawal L., Hongyi C., Bhattacharyya S. Neurodegenerative Disorders of Alzheimer, Parkinsonism, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Multiple Sclerosis: An Early Diagnostic Approach for Precision Treatment. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022;37:67–104. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00800-w. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

