Gellan Gum as a Unique Microbial Polysaccharide: Its Characteristics, Synthesis, and Current Application Trends
- PMID: 38534601
- PMCID: PMC10970089
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10030183
Gellan Gum as a Unique Microbial Polysaccharide: Its Characteristics, Synthesis, and Current Application Trends
Abstract
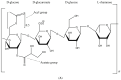
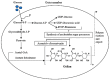
Gellan gum (GG) is a linear, negatively charged exopolysaccharide that is biodegradable and non-toxic. When metallic ions are present, a hard and transparent gel is produced, which remains stable at a low pH. It exhibits high water solubility, can be easily bio-fabricated, demonstrates excellent film/hydrogel formation, is biodegradable, and shows biocompatibility. These characteristics render GG a suitable option for use in food, biomedical, and cosmetic fields. Thus, this review paper offers a concise summary of microbial polysaccharides. Moreover, an in-depth investigation of trends in different facets of GG, such as biosynthesis, chemical composition, and physical and chemical properties, is emphasized. In addition, this paper highlights the process of extracting and purifying GG. Furthermore, an in-depth discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of GG concerning other polysaccharides is presented. Moreover, the utilization of GG across different industries, such as food, medicine, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, etc., is thoroughly examined and will greatly benefit individuals involved in this field who are seeking fresh opportunities for innovative projects in the future.
Keywords: Sphingomonas; application; gellan; gelrite; hydrogels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent trends on gellan gum blends with natural and synthetic polymers: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Apr 1;109:1068-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.099. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29157908 Review.
-
Recent advances in gellan gum-based films and its application in sustainable food packaging: a review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Mar 5:1-22. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2025.2466747. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40045536 Review.
-
Application of Gellan Gum-Based Scaffold for Regenerative Medicine.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1249:15-37. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3258-0_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32602088 Review.
-
Advances in tissue engineering of gellan gum-based hydrogels.Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Jan 15;324:121484. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121484. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Carbohydr Polym. 2024. PMID: 37985043 Review.
-
Effects of fermentation conditions on molecular weight, production, and physicochemical properties of gellan gum.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;279(Pt 3):135304. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135304. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39242009
Cited by
-
Microbial-Derived Biopolymers: A Pathway to Sustainable Civil Engineering.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jan 12;17(2):172. doi: 10.3390/polym17020172. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green biosynthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles incorporated gellan gum hydrogel for biomedical application as wound dressing.Front Chem. 2025 Apr 17;13:1560213. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1560213. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40313399 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Microbial Exopolysaccharides: Present and Future Applications.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 16;14(9):1162. doi: 10.3390/biom14091162. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Gelatin/Chitosan and Chitosan Active Films with Rice Bran Extract for the Preservation of Fresh Pork Meat.Gels. 2025 Apr 30;11(5):338. doi: 10.3390/gels11050338. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40422358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanaka F. Theoretical study of molecular association and thermoreversible gelation in polymers. Polym. J. 2002;34:479–509. doi: 10.1295/polymj.34.479. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources