Tailoring Hydrogel Structures: Investigating the Effects of Multistep Cellulose Defibrillation on Polyvinyl Alcohol Composites
- PMID: 38534630
- PMCID: PMC10970658
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10030212
Tailoring Hydrogel Structures: Investigating the Effects of Multistep Cellulose Defibrillation on Polyvinyl Alcohol Composites
Abstract
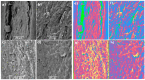
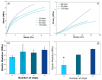
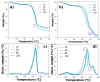
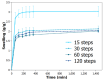
Defibrillating cellulose through various grinding steps and incorporating it into hydrogels introduces unique properties that warrant thorough exploration. This study investigates cellulose defibrillation at different steps (15-120) using an ultra-fine friction grinder, blended with high-molecular-weight polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and crosslinked via freeze-thawing. A critical discovery is the influence of defibrillation on the hydrogel structure, as evidenced by reduced crystallinity, thermal degradation, and the enhanced swelling of PVA chains. Despite an increased elastic modulus of up to 120 steps, the synthesized material maintains remarkable strength under hydrated conditions, holding significant promise in biomaterial applications.
Keywords: PVA; composite hydrogels; freeze–thawing; kraft process; nanofibrillated cellulose.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang K., Su Y., Xiao H. Preparation and characterization of nanofibrillated cellulose from waste sugarcane bagasse by mechanical force. BioResources. 2020;15:6636–6647. doi: 10.15376/biores.15.3.6636-6647. - DOI
-
- Felgueiras H.P., Teixeira M.A., Tavares T.D., Homem N.C., Zille A., Amorim M.T.P. Antimicrobial action and clotting time of thin, hydrated poly(vinyl alcohol)/cellulose acetate films functionalized with LL37 for prospective wound-healing applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020;137:48626. doi: 10.1002/app.48626. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

