Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis Virus Using TaqMan-based qPCR in Eastern China
- PMID: 38535872
- PMCID: PMC10975075
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci11030138
Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis Virus Using TaqMan-based qPCR in Eastern China
Abstract
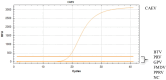
Caprine arthritis encephalitis is an infectious disease caused by the caprine arthritis encephalitis virus that infects goats, sheep, and other small ruminants. An outbreak of CAEV could be extremely harmful to the goat farming industry and could cause severe economic losses. We designed specific primers and probes for the gag gene and established a TaqMan real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay. This method's correlation coefficient (R2) was >0.999, and the sensitivity of the assay to the plasmid-carried partial gag gene was approximately 10 copies/µL, 1000 times higher than that of conventional PCR. No specific fluorescence was detected for other sheep viruses. Using this method, we tested 776 asymptomatic sheep blood samples and 4 neurodegenerative sheep brain samples from six farms in eastern China, and the positivity rate was 0.77% (6/780). The gag gene was partially sequenced in the three positive samples and compared with the sequences from other representative strains in GenBank. The results revealed that all three strains belonged to the B1 subtype and were most closely related to the strains from Shanxi and Gansu, previously isolated in China, with their homology ranging from 97.7% to 98.9%. These results suggest that the designed RT-qPCR assay can be used to detect subclinical CAEV in sheep and that the virus is still present in eastern China.
Keywords: TaqMan RT-qPCR; caprine arthritis encephalitis virus; detecting method; goat; infectious diseases; phylogenetic trees.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Liu D., Qiu Z., Pu F., Lin J., Li J. Serologic diagnosis of Maedi visna. Chin. Vet. Sci. 1990:9–12.
-
- Gong C., Zhou T., Hu Z., Lin J., Yue M. Serologic diagnosis of Maedi visna in Xinjiang (preliminary report) Chin. J. Vet. Med. 1984;12:11–14.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

