A polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor enhances erastin sensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro
- PMID: 38536443
- PMCID: PMC11390781
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-024-04654-8
A polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor enhances erastin sensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro
Abstract
Background: Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a critical therapeutic target in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). The objective of this study was to investigate the therapeutic effect of the combination of BI 2536, a PLK1 inhibitor, and erastin, a ferroptosis inducer, in HNSCC.
Methods: The proliferation, invasion, and migration abilities of Tu177 and FaDu cells upon exposure to BI 2536 and erastin, used in combination or alone, were tested. Fe2+, glutathione (GSH), and malondialdehyde (MDA) detection kits were used to determine whether the addition of BI 2536 enhanced the accumulation of Fe2+ and MDA, along with the depletion of GSH. Quantitative real-time PCR, western blot analyses were performed to investigate whether BI 2536 further altered the mRNA and expression level of ferroptosis genes. Furthermore, si PLK1 was used to investigate whether targeting PLK1 gene promoted erastin-induced ferroptosis.
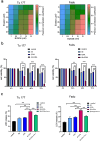
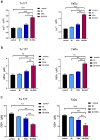
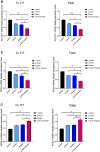
Results: The combination of BI 2536 and erastin exerted a stronger cytotoxicity than treatment with a single agent. Compared with erastin treatment alone, the combination of BI 2536 and erastin lowered the ability of tumor cells to self-clone, invade, and migrate. BI 2536 enhanced the accumulation of Fe2+ and MDA, and the depletion of GSH. BI 2536 increased erastin-induced changes in ferroptosis-related gene mRNA and expression. Importantly, targeting PKL1 enhanced the anti-cancer effect of erastin.
Conclusion: BI 2536 enhanced the sensitivity of HNSCC cells to erastin, which provides a new perspective for cancer treatment.
Keywords: BI 2536; Erastin; HNSCC; PLK1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The author declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inactivation enhances PI3K inhibition-mediated apoptosis of NOTCH1-mutant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2025 Aug 10;625:217814. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217814. Epub 2025 May 22. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 40412794
-
Mutations of the LIM protein AJUBA mediate sensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to treatment with cell-cycle inhibitors.Cancer Lett. 2017 Apr 28;392:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.01.024. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28126323 Free PMC article.
-
The Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor onvansertib represents a relevant treatment for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma resistant to cisplatin and radiotherapy.Theranostics. 2021 Sep 21;11(19):9571-9586. doi: 10.7150/thno.61711. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34646387 Free PMC article.
-
BI_2536--targeting the mitotic kinase Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1).Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010;184:215-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-01222-8_15. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20072841 Review.
-
Research progress on ferroptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Mol Histol. 2025 Mar 17;56(2):109. doi: 10.1007/s10735-025-10381-y. J Mol Histol. 2025. PMID: 40095205 Review.
Cited by
-
Consensus artificial intelligence-driven prognostic signature for predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: a multi-center and large-scale study.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Jul 1;9(1):207. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-01010-8. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40595395 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfidptosis ‒ related lncRNAs are biomarkers of prognosis and immune response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 May 15;91(5):101625. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2025.101625. Online ahead of print. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40378782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Day AT, Sher DJ, Lee RC, Truelson JM, Myers LL, Sumer BD, Stankova L, Tillman BN, Hughes RS, Khan SA, Gordin EA (2020) Head and neck oncology during the COVID-19 pandemic: reconsidering traditional treatment paradigms in light of new surgical and other multilevel risks. Oral Oncol 105:104684. 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104684 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104684 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee NY, Ferris RL, Psyrri A, Haddad RI, Tahara M, Bourhis J, Harrington K, Chang PM-H, Lin J-C, Razaq MA, Teixeira MM, Lövey J, Chamois J, Rueda A, Hu C, Dunn LA, Dvorkin MV, De Beukelaer S, Pavlov D, Thurm H, Cohen E (2021) Avelumab plus standard-of-care chemoradiotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy alone in patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 22:450–462. 10.1016/s1470-2045(20)30737-3 10.1016/s1470-2045(20)30737-3 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

