The role of Na+-coupled bicarbonate transporters (NCBT) in health and disease
- PMID: 38536494
- PMCID: PMC11338471
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-024-02937-w
The role of Na+-coupled bicarbonate transporters (NCBT) in health and disease
Abstract
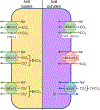
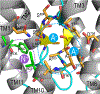
Cellular and organism survival depends upon the regulation of pH, which is regulated by highly specialized cell membrane transporters, the solute carriers (SLC) (For a comprehensive list of the solute carrier family members, see: https://www.bioparadigms.org/slc/ ). The SLC4 family of bicarbonate (HCO3-) transporters consists of ten members, sorted by their coupling to either sodium (NBCe1, NBCe2, NBCn1, NBCn2, NDCBE), chloride (AE1, AE2, AE3), or borate (BTR1). The ionic coupling of SLC4A9 (AE4) remains controversial. These SLC4 bicarbonate transporters may be controlled by cellular ionic gradients, cellular membrane voltage, and signaling molecules to maintain critical cellular and systemic pH (acid-base) balance. There are profound consequences when blood pH deviates even a small amount outside the normal range (7.35-7.45). Chiefly, Na+-coupled bicarbonate transporters (NCBT) control intracellular pH in nearly every living cell, maintaining the biological pH required for life. Additionally, NCBTs have important roles to regulate cell volume and maintain salt balance as well as absorption and secretion of acid-base equivalents. Due to their varied tissue expression, NCBTs have roles in pathophysiology, which become apparent in physiologic responses when their expression is reduced or genetically deleted. Variations in physiological pH are seen in a wide variety of conditions, from canonically acid-base related conditions to pathologies not necessarily associated with acid-base dysfunction such as cancer, glaucoma, or various neurological diseases. The membranous location of the SLC4 transporters as well as recent advances in discovering their structural biology makes them accessible and attractive as a druggable target in a disease context. The role of sodium-coupled bicarbonate transporters in such a large array of conditions illustrates the potential of treating a wide range of disease states by modifying function of these transporters, whether that be through inhibition or enhancement.
Keywords: Animal SLC4 gene evolution; Anion exchange; Bicarbonate; Chloride; Monogenic disease; NBCe; NBCn; NCBT; Na cotransport; SLC4; SLC4 structure; Sodium.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The SLC4 family of bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) transporters.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Apr-Jun;34(2-3):159-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.10.008. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23506864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cation-coupled bicarbonate transporters.Compr Physiol. 2014 Oct;4(4):1605-37. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c130005. Compr Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25428855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The divergence, actions, roles, and relatives of sodium-coupled bicarbonate transporters.Physiol Rev. 2013 Apr;93(2):803-959. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00023.2012. Physiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23589833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The SLC4 family of HCO 3 - transporters.Pflugers Arch. 2004 Feb;447(5):495-509. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1180-2. Epub 2004 Jan 14. Pflugers Arch. 2004. PMID: 14722772 Review.
-
Structure and Function of SLC4 Family [Formula: see text] Transporters.Front Physiol. 2015 Dec 1;6:355. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00355. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26648873 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Beyond SGLT2: proximal tubule transporters as potential drug targets for chronic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2025 Feb 5;40(Supplement_1):i18-i28. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfae211. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2025. PMID: 39907544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complexities, Benefits, Risks, and Clinical Implications of Sodium Bicarbonate Administration in Critically Ill Patients: A State-of-the-Art Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 21;13(24):7822. doi: 10.3390/jcm13247822. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39768744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abuladze N, Lee I, Newman D, Hwang J, Boorer K, Pushkin A, Kurtz I (1998) Molecular Cloning, Chromosomal Localization, Tissue Distribution, and Functional Expression of the Human Pancreatic Sodium Bicarbonate Cotransporter. J Biol Chem 273:17689–17695 - PubMed
-
- Abuladze N, Song M, Pushkin A, Newman D, Lee I, Nicholas S, Kurtz I (2000) Structural organization of the human NBC1 gene: kNBC1 is transcribed from an alternative promoter in intron 3. Gene 251:109–122 - PubMed
-
- Allen DG, Xiao XH (2003) Role of the cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger during ischemia and reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res 57:934–941. doi:S0008636302008362 [pii] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

