Pathologic maternal and neonatal outcomes associated with programmed embryo transfer: potential etiologies and strategies for prevention
- PMID: 38536596
- PMCID: PMC11052758
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-024-03042-8
Pathologic maternal and neonatal outcomes associated with programmed embryo transfer: potential etiologies and strategies for prevention
Abstract
Purpose: In the first of two companion papers, we comprehensively reviewed the recent evidence in the primary literature, which addressed the increased prevalence of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, late-onset or term preeclampsia, fetal overgrowth, postterm birth, and placenta accreta in women conceiving by in vitro fertilization. The preponderance of evidence implicated frozen embryo transfer cycles and, specifically, those employing programmed endometrial preparations, in the higher risk for these adverse maternal and neonatal pregnancy outcomes. Based upon this critical appraisal of the primary literature, we formulate potential etiologies and suggest strategies for prevention in the second article.
Methods: Comprehensive review of primary literature.
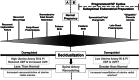
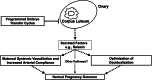
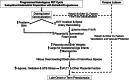
Results: Presupposing significant overlap of these apparently diverse pathological pregnancy outcomes within subjects who conceive by programmed autologous FET cycles, shared etiologies may be at play. One plausible but clearly provocative explanation is that aberrant decidualization arising from suboptimal endometrial preparation causes greater than normal trophoblast invasion and myometrial spiral artery remodeling. Thus, overly robust placentation produces larger placentas and fetuses that, in turn, lead to overcrowding of villi within the confines of the uterine cavity which encroach upon intervillous spaces precipitating placental ischemia, oxidative and syncytiotrophoblast stress, and, ultimately, late-onset or term preeclampsia. The absence of circulating corpus luteal factors like relaxin in most programmed cycles might further compromise decidualization and exacerbate the maternal endothelial response to deleterious circulating placental products like soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 that mediate disease manifestations. An alternative, but not mutually exclusive, determinant might be a thinner endometrium frequently associated with programmed endometrial preparations, which could conspire with dysregulated decidualization to elicit greater than normal trophoblast invasion and myometrial spiral artery remodeling. In extreme cases, placenta accreta could conceivably arise. Though lower uterine artery resistance and pulsatility indices observed during early pregnancy in programmed embryo transfer cycles are consistent with this initiating event, quantitative analyses of trophoblast invasion and myometrial spiral artery remodeling required to validate the hypothesis have not yet been conducted.
Conclusions: Endometrial preparation that is not optimal, absent circulating corpus luteal factors, or a combination thereof are attractive etiologies; however, the requisite investigations to prove them have yet to be undertaken. Presuming that in ongoing RCTs, some or all adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with programmed autologous FET are circumvented or mitigated by employing natural or stimulated cycles instead, then for women who can conceive using these regimens, they would be preferable. For the 15% or so of women who require programmed FET, additional research as suggested in this review is needed to elucidate the responsible mechanisms and develop preventative strategies.
Keywords: Birth weight; Corpus luteum; Decidualization; Endometrium; Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy; In vitro fertilization; Large for gestational age; Macrosomia; Placenta; Placenta accreta; Postterm birth; Preeclampsia; Pregnancy; Relaxin; Spiral artery; Trophoblast.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
KPC holds use patents for relaxin.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

