In silico methods for immunogenicity risk assessment and human homology screening for therapeutic antibodies
- PMID: 38536724
- PMCID: PMC10978032
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2333729
In silico methods for immunogenicity risk assessment and human homology screening for therapeutic antibodies
Abstract
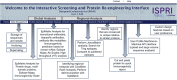
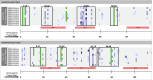
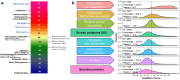
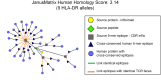
In silico immunogenicity risk assessment has been an important step in the development path for many biologic therapeutics, including monoclonal antibodies. Even if the source of a given biologic is 'fully human', T cell epitopes that are contained in the sequences of the biologic may activate the immune system, enabling the development of anti-drug antibodies that can reduce drug efficacy and may contribute to adverse events. Computational tools that identify T cell epitopes from primary amino acid sequences have been used to assess the immunogenic potential of therapeutic candidates for several decades. To facilitate larger scale analyses and accelerate preclinical immunogenicity risk assessment, our group developed an integrated web-based platform called ISPRI, (Immunogenicity Screening and Protein Re-engineering Interface) that provides hands-on access through a secure web-based interface for scientists working in large and mid-sized biotech companies in the US, Europe, and Japan. This toolkit has evolved and now contains an array of algorithms that can be used individually and/or consecutively for immunogenicity assessment and protein engineering. Most analyses start with the advanced epitope mapping tool (EpiMatrix), then proceed to identify epitope clusters using ClustiMer, and then use a tool called JanusMatrix to define whether any of the T cell epitope clusters may generate a regulatory T cell response which may diminish or eliminate anti-drug antibody formation. Candidates can be compared to similar products on a normalized immunogenicity scale. Should modifications to the biologic sequence be an option, a tool for moderating putative immunogenicity by editing T cell epitopes out of the sequence is available (OptiMatrix). Although this perspective discusses the in-silico immunogenicity risk assessment for monoclonal antibodies, bi-specifics, multi-specifics, and antibody-drug conjugates, the analysis of additional therapeutic modalities such as enzyme replacement proteins, blood factor proteins, CAR-T, gene therapy products, and peptide drugs is also made available on the ISPRI platform.
Keywords: Anti-drug antibodies; EpiMatrix; JanusMatrix; T cell epitope; immunogenicity; immunoinformatics; monoclonal antibody; tregitope.
Plain language summary
ISPRI (Interactive Screening and Protein Reengineering Interface): Integrated, cloud-based, comprehensive toolkit for Immunogenicity Risk Assessment.EpiMatrix Immunogenicity Score: Combined T effector and Treg Epitope Content per unit protein.Tregitopes: Treg Epitopes found in IgG Framework that have been shown to modulate antigen-specific effector T cell responses.ClustiMer: Tool for identifying epitope rich polypeptides from within a given protein sequence.JanusMatrix: Tool for Predicting Tolerance, Putative Treg Epitopes, and Anti-self-immune responses.OptiMatrix: Tool for modifying T cell epitope sequences to reduce (or enhance) MHC binding.
Conflict of interest statement
AD and WM are senior officers and shareholders, and AM, AG, SS, JT, MA, and AR are employees of EpiVax, Inc., a privately owned biotechnology company located in Providence, RI. These authors acknowledge that there is a potential conflict of interest related to their relationship with EpiVax and attest that the work contained in this perspectives article is free of any bias that might be associated with the commercial goals of the company.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Better Epitope Discovery, Precision Immune Engineering, and Accelerated Vaccine Design Using Immunoinformatics Tools.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 7;11:442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00442. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32318055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does human homology reduce the potential immunogenicity of non-antibody scaffolds?Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 7;14:1215939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1215939. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Tolerance-Adjusted Personalized Immunogenicity Prediction for Pompe Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 16;12:636731. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636731. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34220802 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The two-faced T cell epitope: examining the host-microbe interface with JanusMatrix.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013 Jul;9(7):1577-86. doi: 10.4161/hv.24615. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23584251 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cell epitope content in human antibodies decreases during maturation.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 17;16:1535826. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1535826. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40313951 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Heavy chain-only antibodies with a stabilized human VH in transgenic chickens for therapeutic antibody discovery.MAbs. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2435476. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2024.2435476. Epub 2024 Nov 28. MAbs. 2024. PMID: 39607037 Free PMC article.
-
Individual and population-level variability in HLA-DR associated immunogenicity risk of biologics used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2024 May 15;15:1377911. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1377911. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38812524 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Immunogenetic Analysis of Botulinum Toxin A Immunogenicity and HLA Gene Haplotypes: New Insights.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Apr 6;17(4):182. doi: 10.3390/toxins17040182. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278680 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into resistance mechanisms to T cell engagers.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 22;16:1583044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1583044. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40330489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Drug Antibody Response to Therapeutic Antibodies and Potential Mitigation Strategies.Biomedicines. 2025 Jan 26;13(2):299. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020299. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Immunogenicity Assessment for Therapeutic Protein Products . Accessed March 5, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents...
-
- Karle A, Spindeldreher S, Kolbinger F. Secukinumab, a novel anti–IL-17A antibody, shows low immunogenicity potential in human in vitro assays comparable to other marketed biotherapeutics with low clinical immunogenicity. Mabs-austin. 2016;8(3):536–550. doi:10.1080/19420862.2015.1136761. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
