Rapid resurgence of syphilis in Japan after the COVID-19 pandemic: A descriptive study
- PMID: 38536832
- PMCID: PMC10971634
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298288
Rapid resurgence of syphilis in Japan after the COVID-19 pandemic: A descriptive study
Abstract
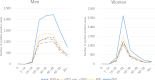
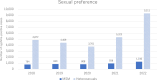
Some countries have reported a post-pandemic resurgence in syphilis prevalence, but trend data in the World Health Organization Western Pacific Region (WHO-WPRO), including Japan, are severely lacking. Thus, the present study compares the number of syphilis cases before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in some WHO-WPRO countries. In addition, temporal trends in the number of syphilis cases in Japan pre- and post-pandemic are described. Annual numbers of syphilis cases during the study periods from China, New Zealand, Australia and Japan were compared. Annual trends of the numbers of syphilis cases during the same study periods were examined in Japan. In 2020, the number of syphilis-positive cases decreased in all four countries. In 2021, though, China, Australia and Japan all showed an increase in the numbers of syphilis cases. However, the rate of increase in China (+2.8%) and Australia (+4.8%) was low compared to Japan (+36.0%). The number of syphilis cases in New Zealand in 2021 was 12.6% lower than in 2020. In 2022, the number of cases of syphilis in China was 7.4% lower than in 2021. The increase of syphilis-positive cases was approximately 6.3-fold higher in Japan compared to Australia (+66.2% vs. +10.5%) in 2022. In conclusion, post-pandemic resurgence of syphilis occurred in Australia and Japan, but not in China and New Zealand. The reason for the substantial increase in syphilis-positive cases in Japan remains unclear. Post-pandemic, prevention and control of sexually transmitted infections still require attention.
Copyright: © 2024 Komori et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization department news. STIs in 2022: emerging and re-emerging outbreaks. 2 September 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/02-09-2022-stis-in-2022-emerging-and-re-em.... Accessed: 9 February 2023.
-
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Infectious syphilis and congenital syphilis in Canada, 2021. December 2022. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/reports-publications/can.... Accessed: 9 February 2023.
-
- National Institute of Infectious Diseases. National institute of infectious diseases home page. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/en/. Accessed: 17 January 2024. In Japanese.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

