Lupus susceptibility gene Pbx1 controls the development, stability, and function of regulatory T cells via Rtkn2 expression
- PMID: 38536923
- PMCID: PMC10971436
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi4310
Lupus susceptibility gene Pbx1 controls the development, stability, and function of regulatory T cells via Rtkn2 expression
Abstract
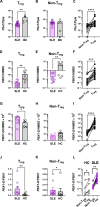
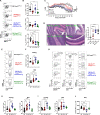
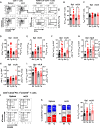
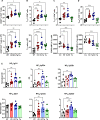
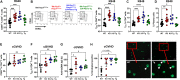
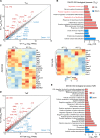
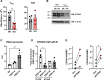
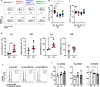
The maintenance of regulatory T (Treg) cells critically prevents autoimmunity. Pre-B cell leukemia transcription factor 1 (Pbx1) variants are associated with lupus susceptibility, particularly through the expression of a dominant negative isoform Pbx1-d in CD4+ T cells. Pbx1-d overexpression impaired Treg cell homeostasis and promoted inflammatory CD4+ T cells. Here, we showed a high expression of Pbx1 in human and murine Treg cells, which is decreased in lupus patients and mice. Pbx1 deficiency or Pbx1-d overexpression reduced the number, stability, and suppressive activity of Treg cells, which increased murine responses to immunization and autoimmune induction. Mechanistically, Pbx1 deficiency altered the expression of genes implicated in cell cycle and apoptosis in Treg cells. Intriguingly, Rtkn2, a Rho-GTPase previously associated with Treg homeostasis, was directly transactivated by Pbx1. Our results suggest that the maintenance of Treg cell homeostasis and stability by Pbx1 through cell cycle progression prevent the expansion of inflammatory T cells that otherwise exacerbates lupus progression in the hosts.
Figures
References
-
- Wing K., Sakaguchi S., Regulatory T cells exert checks and balances on self tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 11, 7–13 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Jordan M. S., Boesteanu A., Reed A. J., Petrone A. L., Holenbeck A. E., Lerman M. A., Naji A., Caton A. J., Thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells induced by an agonist self-peptide. Nat. Immunol. 2, 301–306 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Ohkura N., Hamaguchi M., Morikawa H., Sugimura K., Tanaka A., Ito Y., Osaki M., Tanaka Y., Yamashita R., Nakano N., Huehn J., Fehling H. J., Sparwasser T., Nakai K., Sakaguchi S., T cell receptor stimulation-induced epigenetic changes and Foxp3 expression are independent and complementary events required for Treg cell development. Immunity 37, 785–799 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

