Impact of skeletal muscle mass on postoperative complications in oral cancer surgery
- PMID: 38538802
- PMCID: PMC10973294
- DOI: 10.1186/s40902-024-00417-w
Impact of skeletal muscle mass on postoperative complications in oral cancer surgery
Abstract
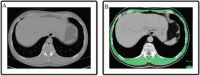
Background: Sarcopenia is characterized by a progressive and generalized loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength. The aim of this retrospective study was to investigate the impact of skeletal muscle mass on adverse events in free-flap reconstruction for defects after oral cancer resection.
Results: Of 120 patients, recipient-site adverse events occurred in 56 patients (46.7%), and recipient-site surgical site infections occurred in 45 patients (37.5%). Skeletal muscle index was significantly associated with recipient-site adverse events in univariate analysis (P < 0.05). Lower body mass index and skeletal muscle index were significantly associated with recipient-site surgical site infection in univariate analysis (P < 0.05). In the multiple logistic regression model, a lower skeletal muscle index was a significant risk factor for recipient-site adverse events and surgical site infections (adverse events odds ratio; 3.17/P = 0.04; surgical site infection odds ratio; 3.76/P = 0.02).
Conclusions: The SMI at level Th12 was an independent factor for postoperative AEs, especially SSI, in OSCC patients with free-flap reconstruction.
Keywords: Oral cancer; Postoperative adverse events; Sarcopenia; Skeletal muscle mass; Surgical site infection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenberg IH. Summary comments. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989;50:1231–1233. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/50.5.1231. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources