Reduction of false positives using zone-specific prostate-specific antigen density for prostate MRI-based biopsy decision strategies
- PMID: 38538841
- PMCID: PMC11399225
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-024-10700-z
Reduction of false positives using zone-specific prostate-specific antigen density for prostate MRI-based biopsy decision strategies
Abstract
Objectives: To develop and test zone-specific prostate-specific antigen density (sPSAD) combined with PI-RADS to guide prostate biopsy decision strategies (BDS).
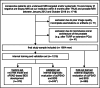
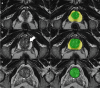
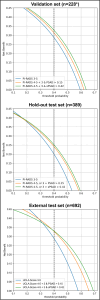
Methods: This retrospective study included consecutive patients, who underwent prostate MRI and biopsy (01/2012-10/2018). The whole gland and transition zone (TZ) were segmented at MRI using a retrained deep learning system (DLS; nnU-Net) to calculate PSAD and sPSAD, respectively. Additionally, sPSAD and PI-RADS were combined in a BDS, and diagnostic performances to detect Grade Group ≥ 2 (GG ≥ 2) prostate cancer were compared. Patient-based cancer detection using sPSAD was assessed by bootstrapping with 1000 repetitions and reported as area under the curve (AUC). Clinical utility of the BDS was tested in the hold-out test set using decision curve analysis. Statistics included nonparametric DeLong test for AUCs and Fisher-Yates test for remaining performance metrics.
Results: A total of 1604 patients aged 67 (interquartile range, 61-73) with 48% GG ≥ 2 prevalence (774/1604) were evaluated. By employing DLS-based prostate and TZ volumes (DICE coefficients of 0.89 (95% confidence interval, 0.80-0.97) and 0.84 (0.70-0.99)), GG ≥ 2 detection using PSAD was inferior to sPSAD (AUC, 0.71 (0.68-0.74)/0.73 (0.70-0.76); p < 0.001). Combining PI-RADS with sPSAD, GG ≥ 2 detection specificity doubled from 18% (10-20%) to 43% (30-44%; p < 0.001) with similar sensitivity (93% (89-96%)/97% (94-99%); p = 0.052), when biopsies were taken in PI-RADS 4-5 and 3 only if sPSAD was ≥ 0.42 ng/mL/cc as compared to all PI-RADS 3-5 cases. Additionally, using the sPSAD-based BDS, false positives were reduced by 25% (123 (104-142)/165 (146-185); p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Using sPSAD to guide biopsy decisions in PI-RADS 3 lesions can reduce false positives at MRI while maintaining high sensitivity for GG ≥ 2 cancers.
Clinical relevance statement: Transition zone-specific prostate-specific antigen density can improve the accuracy of prostate cancer detection compared to MRI assessments alone, by lowering false-positive cases without significantly missing men with ISUP GG ≥ 2 cancers.
Key points: • Prostate biopsy decision strategies using PI-RADS at MRI are limited by a substantial proportion of false positives, not yielding grade group ≥ 2 prostate cancer. • PI-RADS combined with transition zone (TZ)-specific prostate-specific antigen density (PSAD) decreased the number of unproductive biopsies by 25% compared to PI-RADS only. • TZ-specific PSAD also improved the specificity of MRI-directed biopsies by 9% compared to the whole gland PSAD, while showing identical sensitivity.
Keywords: Clinical decision-making; Image-guided biopsy; Magnetic resonance imaging; Prostate-specific antigen density; Prostatic neoplasms.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies, which however did not influence the presented study: A.R.P. Stockholder of Lucida, speakers beaureu for Siemens and research support of Siemens; L.J.S., P.A., B.H., and T.P. receive research grants from the Collaborative Research Center (CRC) 1340 “Matrix in Vision” funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). L.J.S. Research grants, travel stipends, and lecture honoraria from Guerbet; B.H. Consulting fees from Canon/Toshiba; travel support from Canon and Bayer; stock options from pharmaceutical and medical technology companies. T.P. AGO, Aprea AB, ARCAGY-GINECO, Astellas Pharma Global Inc. (APGD), Astra Zeneca, Clovis Oncology, Dohme Corp, Holaira, Incyte Corporation, Karyopharm, Lion Biotechnologies, MedImmune, Merck Sharp, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Morphotec Inc., NovoCure Ltd., PharmaMar S.A. and PharmaMar USA, Roche, Siemens Healthineers, and TESARO.
Prof. Bernd Hamm is the Editor-in-Chief of
Figures

Comment in
-
Refining clinical decision strategies and prostate cancer detection through fine adjustments in the combination of PSA-derived parameters and MRI.Eur Radiol. 2024 Oct;34(10):6227-6228. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10734-3. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38683387 No abstract available.
References
-
- NICE Guideline NG131. Prostate caner: diagnosis and management. Updated December 15th 2021. Accessed September 1, 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

