Image-Guided Percutaneous Drainage of Abdominal Abscesses in Pediatric Patients
- PMID: 38539325
- PMCID: PMC10969118
- DOI: 10.3390/children11030290
Image-Guided Percutaneous Drainage of Abdominal Abscesses in Pediatric Patients
Abstract
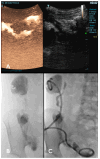
Image-guided percutaneous abscess drainage (IPAD) is an effective, minimally invasive technique to manage infected abdominal fluid collections in children. It is the treatment of choice in cases where surgery is not immediately required due to another coexisting indication. The skills and equipment needed for this procedure are widely available. IPAD is typically guided by ultrasound, fluoroscopy, computed tomography, or a combination thereof. Abscesses in hard-to-reach locations can be drained by intercostal, transhepatic, transgluteal, transrectal, or transvaginal approaches. Pediatric IPAD has a success rate of over 80% and a low complication rate.
Keywords: Seldinger technique; appendicitis; children; pediatrics; percutaneous abscess drainage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wallace M.J., Chin K.W., Fletcher T.B., Bakal C.W., Cardella J.F., Grassi C.J., Grizzard J.D., Kaye A.D., Kushner D.C., Larson P.A., et al. Quality Improvement Guidelines for Percutaneous Drainage/Aspiration of Abscess and Fluid Collections. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010;21:431–435. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2009.12.398. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Sonnenberg E., Wittich G.R., Edwards D.K., Casola G., von Waldenburg Hilton S., Self T.W., Keightley A., Withers C. Percutaneous Diagnostic and Therapeutic Interventional Radiologic Procedures in Children: Experience in 100 Patients. Radiology. 1987;162:601–605. doi: 10.1148/radiology.162.3.2949336. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

