Machine Learning Meets Cancer
- PMID: 38539435
- PMCID: PMC10969040
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16061100
Machine Learning Meets Cancer
Abstract
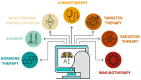
The role of machine learning (a part of artificial intelligence-AI) in the diagnosis and treatment of various types of oncology is steadily increasing. It is expected that the use of AI in oncology will speed up both diagnostic and treatment planning processes. This review describes recent applications of machine learning in oncology, including medical image analysis, treatment planning, patient survival prognosis, and the synthesis of drugs at the point of care. The fast and reliable analysis of medical images is of great importance in the case of fast-flowing forms of cancer. The introduction of ML for the analysis of constantly growing volumes of big data makes it possible to improve the quality of prescribed treatment and patient care. Thus, ML is expected to become an essential technology for medical specialists. The ML model has already improved prognostic prediction for patients compared to traditional staging algorithms. The direct synthesis of the necessary medical substances (small molecule mixtures) at the point of care could also seriously benefit from the application of ML. We further review the main trends in the use of artificial intelligence-based technologies in modern oncology. This review demonstrates the future prospects of using ML tools to make progress in cancer research, as well as in other areas of medicine. Despite growing interest in the use of modern computer technologies in medical practice, a number of unresolved ethical and legal problems remain. In this review, we also discuss the most relevant issues among them.
Keywords: PET/CT; artificial intelligence; machine learning; oncology; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Klauschen F., Müller K.R., Binder A., Bockmayr M., Hägele M., Seegerer P., Wienert S., Pruneri G., de Maria S., Badve S., et al. Scoring of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: From visual estimation to machine learning. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018;52:151–157. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.07.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kazmierska J., Hope A., Spezi E., Beddar S., Nailon W.H., Osong B., Ankolekar A., Choudhury A., Dekker A., Redalen K.R., et al. From multisource data to clinical decision aids in radiation oncology: The need for a clinical data science community. Radiother. Oncol. 2020;153:43–54. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.09.054. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources