Enhancing Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities in Bee-Collected Pollen through Solid-State Fermentation: A Comparative Analysis of Bioactive Compounds
- PMID: 38539826
- PMCID: PMC10967301
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13030292
Enhancing Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities in Bee-Collected Pollen through Solid-State Fermentation: A Comparative Analysis of Bioactive Compounds
Abstract
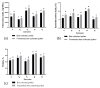
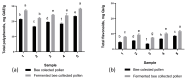
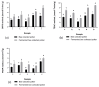
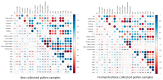
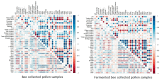
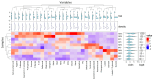
The present study investigates the impact of solid-state fermentation on bee-collected pollen using a consortium of Lactobacillus plantarum, Apilactobacillus kunkeei, and Lactobacillus acidophilus. Another aim is to compare the nutritional and bioactive properties of natural versus fermented pollen, focusing on macronutrient composition, pH, acidity, lactic acid content, and profiles of polyphenolics and flavonoids. Our results indicated significant enhancements in the contents of amino acids, suggesting improved protein content, alongside increases in polyphenolic and flavonoid contents post-fermentation. According to the heat mapping and cluster analysis, increased antioxidant and antimicrobial activities against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, particularly E. coli, were observed in the fermented bee-collected pollen samples, which may have been due to the accumulation of phenolic compounds (e.g., ellagic acid, kaempferol, quercetin, and quercetin-3-O-rutinoside). Furthermore, significant positive correlations of the fermented bee-collected pollen samples with non-essential amino acids were recorded compared with the unfermented bee-collected pollen samples, which may have been due to the fermentation process and the conversion of proteins into free amino acids via proteolysis. Future research could explore the underlying mechanisms, the scalability of fermentation, its application in functional foods, and the health benefits of fermented bee-collected pollen in human diets.
Keywords: amino acids; antimicrobial activity; antioxidant activity; bee-collected pollen; fermentation; lactic acid bacteria; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors N.K.O. and R.F.B. are affiliated with SC PlantExtrakt SRL; however, SC PlantExtrakt SRL had no role in the financing or design of this study and did not in any way influence the results of this study or the decision to publish the data obtained. The remaining authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be interpreted as potential conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Mǎrghitaş L.A., Stanciu O.G., Dezmirean D.S., Bobiş O., Popescu O., Bogdanov S., Campos M.G. In Vitro Antioxidant Capacity of Honeybee-Collected Pollen of Selected Floral Origin Harvested from Romania. Food Chem. 2009;115:878–883. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.01.014. - DOI
-
- Mărgăoan R., Zăhan M., Mărghitaş L.A., Dezmirean D.S., Erler S., Bobiş O. Antiproliferative Activity and Apoptotic Effects of Filipendula Ulmaria Pollen against C26 Mice Colon Tumour Cells. J. Apic. Sci. 2016;60:135–144. doi: 10.1515/jas-2016-0014. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

