Analysis of Primary Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells' Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 38540136
- PMCID: PMC10968363
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12030524
Analysis of Primary Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells' Signaling Pathways
Abstract
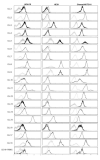
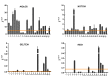
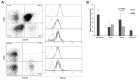
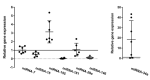
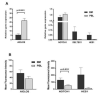
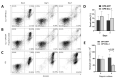
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by a specific expansion of mature B-cell clones. We hypothesized that the disease has a heterogeneous clinical outcome that depends on the genes and signaling pathways active in the malignant clone of the individual patient. It was found that several signaling pathways are active in CLL, namely, NOTCH1, the Ikaros family genes, BCL2, and NF-κB, all of which contribute to cell survival and the proliferation of the leukemic clone. Therefore, we analyzed primary CLL cells for the gene and protein expression of NOTCH1, DELTEX1, HES1, and AIOLOS in both peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) and the bone marrow (BM) of patients, as well as the expression of BCL2 and miRNAs to see if they correlate with any of these genes. BCL2 and AIOLOS were highly expressed in all CLL samples as previously described, but we show here for the first time that AIOLOS expression was higher in the PBLs than in the BM. On the other hand, NOTCH1 activation was higher in the BM. In addition, miR-15a, miR-181, and miR-146 were decreased and miR-155 had increased expression in most samples. The activation of the NOTCH pathway in vitro increases the susceptibility of primary CLL cells to apoptosis despite high BCL2 expression.
Keywords: AIOLOS; BCL-2; CLL; NOTCH; leukemia; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hes1 Controls Proliferation and Apoptosis in Chronic Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells by Modulating PTEN Expression.Mol Biotechnol. 2022 Dec;64(12):1419-1430. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00476-2. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Mol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35704163
-
Deregulation of Aiolos expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is associated with epigenetic modifications.Blood. 2011 Feb 10;117(6):1917-27. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-307140. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21139082
-
[Expression of Notch Gene and Its Role of Anti-apoptosis and Drug-resistance of Cells in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Aug;23(4):919-24. doi: 10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2015.04.002. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26314418 Chinese.
-
Evaluation of MiR-15a and MiR-16-1 as prognostic biomarkers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Aug;92:864-869. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.144. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28599250 Review.
-
BCL-2 Inhibition as Treatment for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021 Jun 10;22(8):66. doi: 10.1007/s11864-021-00862-z. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34110507 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Notch signaling pathways with natural bioactive compounds: a promising approach against cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 18;15:1412669. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1412669. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39092224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kikushige Y., Ishikawa F., Miyamoto T., Shima T., Urata S., Yoshimoto G., Mori Y., Iino T., Yamauchi T., Eto T., et al. Self-renewing hematopoietic stem cell is the primary target in pathogenesis of human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:246–259. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.029. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

