In Vivo Study on Doxycycline Protective Mechanisms during Myocardial Ischemia Injury in Rats
- PMID: 38540247
- PMCID: PMC10967757
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12030634
In Vivo Study on Doxycycline Protective Mechanisms during Myocardial Ischemia Injury in Rats
Abstract
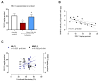
Background: The fact that during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, myosin light chain 1 (MLC1) and troponin I (TnI) are degraded by matrix metalloproteases activity has already been well established in both in vitro and ex vivo studies. However, I/R injury is a complex issue based on several overlapping mechanisms. Increased activity of myosin light chain kinase and nitric oxide synthase due to oxidative stress leads to post-translational modifications of MLC1, thus leading to the increased degradation of these proteins.
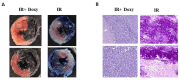
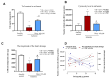
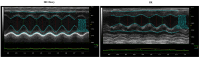
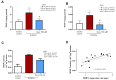
Methods: Wistar rats were subjected to left anterior descending coronary artery occlusion. To measure the pharmacological effect of doxycycline, transthoracic echocardiography as well as biochemical tests, concentrations of TnI, LDH, MLC1, MMP-2 and MMP-9 were performed. Gelatinize activity and cytotoxicity level were also assessed; Results: I.p., administration of doxycycline before LAD occlusion surgery increased TnI and LDH content in the heart and decreased cytotoxicity. A reduction of MMP-2 and MMP-9 concentration and MMP-2 activity after administration of Doxy was also observed, as well as improvement in echocardiographic parameters just 7 days after surgery.
Conclusions: Inhibition of MMPs by doxycycline, in vivo, may serve as a protective agent in future therapy.
Keywords: LAD; MLC1; MMPs; doxycycline; ischemic heart disease; rat myocardial infraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
L-NAME improves doxycycline and ML-7 cardioprotection from oxidative stress.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018 Jan 1;23(2):298-309. doi: 10.2741/4592. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018. PMID: 28930548
-
Combined subthreshold dose inhibition of myosin light chain phosphorylation and MMP-2 activity provides cardioprotection from ischaemic/reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;170(2):380-90. doi: 10.1111/bph.12289. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23822644 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemia/reperfusion-induced myosin light chain 1 phosphorylation increases its degradation by matrix metalloproteinase 2.FEBS J. 2012 Jul;279(13):2444-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08622.x. Epub 2012 Jun 12. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22564771 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect of inhibitors of MMPs and ROS-dependent modifications of contractile proteins on protection hearts subjected to oxidative stress.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(9):1345-8. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990556. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23978100 Review.
-
Intracellular regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity: new strategies in treatment and protection of heart subjected to oxidative stress.Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:130451. doi: 10.1155/2013/130451. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013. PMID: 24455428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The interplay of senescence and MMPs in myocardial infarction: implications for cardiac aging and therapeutics.Biogerontology. 2025 Jan 20;26(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s10522-025-10190-6. Biogerontology. 2025. PMID: 39832057 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

