Putting Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders within the Spectrum of Inflammatory Disorders Can Improve Classification and Diagnostics of These Disorders
- PMID: 38540315
- PMCID: PMC10967747
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12030702
Putting Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders within the Spectrum of Inflammatory Disorders Can Improve Classification and Diagnostics of These Disorders
Abstract
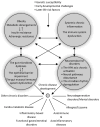
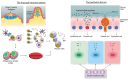
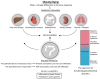
The spectrum, intensity, and overlap of symptoms between functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) and other gastrointestinal disorders characterize patients with FGIDs, who are incredibly different in their backgrounds. An additional challenge with regard to the diagnosis of FGID and the applicability of a given treatment is the ongoing expansion of the risk factors believed to be connected to these disorders. Many cytokines and inflammatory cells have been found to cause the continuous existence of a low level of inflammation, which is thought to be a basic pathophysiological process. The idea of the gut-brain axis has been created to offer a basic framework for the complex interactions that occur between the nervous system and the intestinal functions, including the involvement of gut bacteria. In this review paper, we intend to promote the hypothesis that FGIDs should be seen through the perspective of the network of the neuroendocrine, immunological, metabolic, and microbiome pathways. This hypothesis arises from an increased understanding of chronic inflammation as a systemic disorder, that is omnipresent in chronic health conditions. A better understanding of inflammation's role in the pathogenesis of FGIDs can be achieved by clustering markers of inflammation with data indicating symptoms, comorbidities, and psycho-social factors. Finding subclasses among related entities of FGIDs may reduce patient heterogeneity and help clarify the pathophysiology of this disease to allow for better treatment.
Keywords: chronic diseases; cytokines; functional gastrointestinal disorders; gastrointestinal diseases; gastrointestinal microbiome; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for functional gastrointestinal disorders and inflammatory bowel disease: narrative review of the evidence and potential mechanisms involving the brain-gut axis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 17;15:1444922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1444922. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39355776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is there a causal link between psychological disorders and functional gastrointestinal disorders?Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Nov;14(11):1047-1059. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2020.1801414. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32715790 Review.
-
Digital Therapeutics Care Utilizing Genetic and Gut Microbiome Signals for the Management of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Results From a Preliminary Retrospective Study.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 21;13:826916. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.826916. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35391720 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota dysbiosis in functional gastrointestinal disorders: Underpinning the symptoms and pathophysiology.JGH Open. 2021 Mar 23;5(9):976-987. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12528. eCollection 2021 Sep. JGH Open. 2021. PMID: 34584964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased prevalence of functional gastrointestinal disorders in panic disorder: clinical and theoretical implications.CNS Spectr. 2005 Nov;10(11):899-908. doi: 10.1017/s1092852900019878. CNS Spectr. 2005. PMID: 16273019
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

