High-Quality Assembly and Analysis of the Complete Mitogenomes of German Chamomile (Matricaria recutita) and Roman Chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile)
- PMID: 38540360
- PMCID: PMC10970603
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15030301
High-Quality Assembly and Analysis of the Complete Mitogenomes of German Chamomile (Matricaria recutita) and Roman Chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile)
Abstract
German chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) and Roman chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile) are the two well-known chamomile species from the Asteraceae family. Owing to their essential oils and higher medicinal value, these have been cultivated widely across Europe, Northwest Asia, North America, and Africa. Regarding medicinal applications, German chamomile is the most commonly utilized variety and is frequently recognized as the "star among medicinal species". The insufficient availability of genomic resources may negatively impact the progression of chamomile industrialization. Chamomile's mitochondrial genome is lacking in extensive empirical research. In this study, we achieved the successful sequencing and assembly of the complete mitochondrial genome of M. chamomilla and C. nobile for the first time. An analysis was conducted on codon usage, sequence repeats within the mitochondrial genome of M. chamomilla and C. nobile. The phylogenetic analysis revealed a consistent positioning of M. chamomilla and C. nobile branches within both mitochondrial and plastid-sequence-based phylogenetic trees. Furthermore, the phylogenetic analysis also showed a close relationship between M. chamomilla and C. nobile within the clade comprising species from the Asteraceae family. The results of our analyses provide valuable resources for evolutionary research and molecular barcoding in chamomile.
Keywords: Chamaemelum nobile; Matricaria chamomilla; mitochondrial genome; phylogenetic analysis; repetitive sequence analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

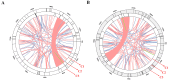
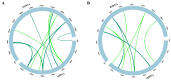
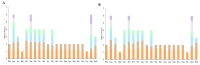
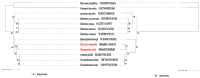
References
-
- Sharafzadeh S., Alizadeh O. German and Roman chamomile. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011;1:01–05.
-
- Zadeh J.B., Kor N.M., Kor Z.M. Chamomile (Matricaria recutita) as a valuable medicinal plant. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2014;2:823–829.
-
- Tai Y., Ling C., Wang C., Wang H., Su L., Yang L., Jiang W., Yu X., Zheng L., Feng Z. Analysis of terpenoid biosynthesis pathways in German chamomile (Matricaria recutita) and Roman chamomile (Chamaemelum nobile) based on co-expression networks. Genomics. 2020;112:1055–1064. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2019.10.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

