Influence of Relative Age on Physical Condition and Academic Performance in Adolescents
- PMID: 38540484
- PMCID: PMC10968513
- DOI: 10.3390/bs14030181
Influence of Relative Age on Physical Condition and Academic Performance in Adolescents
Abstract
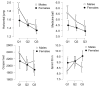
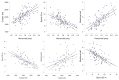
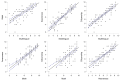
Annual age grouping is a common organizational strategy in academics and sports. This strategy could promote the relative effects of age, which refers to the (dis)advantages that subjects who were born in the first or last months of the year may suffer. The consequences could be minimized, resulting in better physical and/or academic results. The objective of the study was to evaluate the influence of the quarter of birth and examine the correlation between physical condition variables and academic performance. The sample included 79 students (51.90% females) 13.46 ± 0.21 years old in the second year of Obligatory Secondary Education. The physical variables of this study were explosive power, cardiorespiratory capacity, speed, flexibility, and muscle strength. They were evaluated using the horizontal jump tests, Cooper test, 50 m sprint, sit-and-reach test, and medicine ball exercises, respectively. The academic variables were obtained from the average academic grade, grouped by key competencies. An Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA), controlling for gender, body mass, and height, revealed significant differences between male students born in the first quarter compared to those born in subsequent quarters in all physical condition variables (except for cardiorespiratory capacity). For female students, significant differences were observed only in the explosive power variable. No statistically significant intra-sex differences were evident in academic performance at any time of measurement. Additionally, moderate to large correlations were found in the physical condition and academic variables. It is concluded in relation to the need to implement diverse strategies regarding the process of developing physical conditions in adolescence that satisfy the growth needs of students based on age and sex.
Keywords: age differences; developmental differences; education; performance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mavilidi M.F., Marsh H.W., Xu K.M., Parker P.D., Jansen P.W., Paas F. Relative Age Effects on Academic Achievement in the First Ten Years of Formal Schooling: A Nationally Representative Longitudinal Prospective Study. J. Educ. Psychol. 2022;114:308–325. doi: 10.1037/edu0000681. - DOI
-
- Cobley S., McKenna J., Baker J., Wattie N. How Pervasive Are Relative Age Effects in Secondary School Education? J. Educ. Psychol. 2009;101:520–528. doi: 10.1037/a0013845. - DOI
-
- Caye A., Petresco S., de Barros A.J.D., Bressan R.A., Gadelha A., Gonçalves H., Manfro A.G., Matijasevich A., Menezes A.M.B., Miguel E.C., et al. Relative Age and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Data From Three Epidemiological Cohorts and a Meta-analysis. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2020;59:990–997. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2019.07.939. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dhuey E., Lipscomb S. What makes a leader? Relative age and high school leadership. Econ. Educ. Rev. 2008;27:173–183. doi: 10.1016/j.econedurev.2006.08.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

