Zein-Derived Peptides from Corn Promote the Proliferation of C2C12 Myoblasts via Crosstalk of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 38540908
- PMCID: PMC10970237
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13060919
Zein-Derived Peptides from Corn Promote the Proliferation of C2C12 Myoblasts via Crosstalk of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
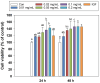
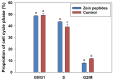
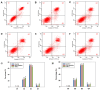
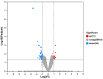
Dietary protein supplementation has emerged as a promising strategy in combating sarcopenia. Furthermore, searching for alternatives of animal proteins has been a hot topic. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of zein peptides on C2C12 myoblasts and explore their potential molecular mechanisms. The proliferative, cell cycle, and anti-apoptotic activities of zein peptides were evaluated. Peptidomics analysis and transcriptome sequencing were employed to explore the structure-activity relationship and underlying molecular mechanisms. The results indicated that zein peptides (0.05-0.2 mg/mL) exerted a significant proliferation-promoting impact on C2C12 cells, via increasing cell viability by 33.37 to 42.39%. Furthermore, zein peptides significantly increased S phase proportion and decreased the apoptosis rate from 34.08% (model group) to 28.96% in C2C12 cells. In addition, zein peptides exhibited a pronounced anti-apoptotic effect on C2C12 cells. Zein peptides are abundant in branch-chain amino acids, especially leucine. Transcriptomics analysis revealed that zein peptides can promote proliferation, accelerate cell cycle, and improve protein synthesis of muscle cells through mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling pathways.
Keywords: anti-apoptotic; cell cycle; cell proliferation; mTOR pathway; molecular mechanism; myoblast; zein peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lin C.C., Ou H.Y., Hsu H.Y., Cheng K.P., Hsieh T.J., Yeh C.H., Su F.C., Kuo L.C. Beyond sarcopenia: Older adults with type II diabetes mellitus tend to experience an elevated risk of poor dynamic balance-a case-control study. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22:138. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-02826-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 32101980/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32001766/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- cstc2021jcyj-msxmX1014/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0304/Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing
- ZJ-2020-09/Open Project Program of China-Canada Joint Lab of Food Nutrition and Health, Beijing Tech-nology and Business University
- SWU-KQ22023/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China
- CQMAITS202313/Chongqing Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System
- KJQN202100225/Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission
- S202310635164/Innovation Training Program for College Students at Southwest University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

