Recycled or Bio-Based Solvents for the Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles: Characterization and Validation in Organic Solar Cells
- PMID: 38541486
- PMCID: PMC10971963
- DOI: 10.3390/ma17061332
Recycled or Bio-Based Solvents for the Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles: Characterization and Validation in Organic Solar Cells
Abstract
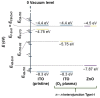
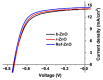
Among solution-processable metal oxides, zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticle inks are widely used in inverted organic solar cells for the preparation, at relatively low temperatures (<120 °C), of highly efficient electron-transporting layers. There is, however, a recent interest to develop more sustainable and less impacting methods/strategies for the preparation of ZnO NPs with controlled properties and improved performance. To this end, we report here the synthesis and characterization of ZnO NPs obtained using alternative reaction solvents derived from renewable or recycled sources. In detail, we use (i) recycled methanol (r-MeOH) to close the loop and minimize wastes or (ii) bioethanol (b-EtOH) to prove the effectiveness of a bio-based solvent. The effect of r-MeOH and b-EtOH on the optical, morphological, and electronic properties of the resulting ZnO NPs, both in solution and thin-films, is investigated, discussed, and compared to an analogous reference material. Moreover, to validate the properties of the resulting materials, we have prepared PTB7:PC71BM-based solar cells containing the different ZnO NPs as a cathode interlayer. Power conversion efficiencies comparable to the reference system (≈7%) were obtained, validating the proposed alternative and more sustainable approach.
Keywords: ZnO nanoparticles; electron-transporting layer; organic solar cells; recycled or bio-based solvents; solution processing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coating ZnO nanoparticle films with DNA nanolayers for enhancing the electron extracting properties and performance of polymer solar cells.Nanoscale. 2017 Dec 14;9(48):19031-19038. doi: 10.1039/c7nr06982k. Nanoscale. 2017. PMID: 29186235
-
Highly efficient inverted polymer solar cells by using solution processed MgO/ZnO composite interfacial layers.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021 Feb 1;583:178-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.047. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021. PMID: 33002690
-
Improved Device Performance of Polymer Solar Cells by Using a Thin Light-harvesting-Complex Modified ZnO Film as the Cathode Interlayer.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Sep 2;7(34):18904-8. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b05969. Epub 2015 Aug 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26292068
-
Composite Interlayer Consisting of Alcohol-Soluble Polyfluorene and Carbon Nanotubes for Efficient Polymer Solar Cells.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Mar 25;12(12):14244-14253. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b22933. Epub 2020 Mar 6. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32075367
-
Solvents induced ZnO nanoparticles aggregation associated with their interfacial effect on organic solar cells.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014 Oct 22;6(20):18172-9. doi: 10.1021/am5051789. Epub 2014 Oct 13. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014. PMID: 25269149
References
-
- Mandal A.K., Katuwal S., Tettey F., Gupta A., Bhattarai S., Jaisi S., Bhandari D.P., Shah A.K., Bhattarai N., Parajuli N. Current Research on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials. 2022;12:3066. doi: 10.3390/nano12173066. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albonetti C., El Qacemi V., Limage S., Versini C., Kauffmann L.D., Muccini M., Seri M. Enhanced Thermal Stability of Inverted Polymer Solar Cells Based on Solution-Processed WOx as an Anode Interlayer. Phys. Status Solidi (A) Appl. Mater. Sci. 2021;218:2000748. doi: 10.1002/pssa.202000748. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

